Combined Administration of Human Ghrelin and Human Growth Hormone Attenuates Organ Injury and Improves Survival in Aged Septic Rats
- PMID: 26835699
- PMCID: PMC5004717
- DOI: 10.2119/molmed.2015.00255
Combined Administration of Human Ghrelin and Human Growth Hormone Attenuates Organ Injury and Improves Survival in Aged Septic Rats
Abstract
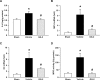
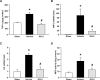
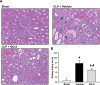
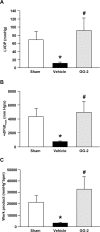
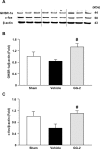
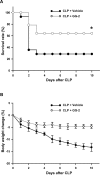
Sepsis is a major healthcare concern, especially in the elderly population. The use of an animal model closely resembling clinical conditions in this population may provide a better prediction in translating bench studies to the bedside. Ghrelin inhibits sympathetic nerve activity and inflammation in young septic animals; however, aged animals become hyporesponsive to ghrelin. In this study, we evaluated the efficacy of combined human ghrelin and growth hormone (GH) for sepsis treatment in the elderly utilizing a clinically relevant animal model of sepsis. Male Fischer 344 rats 22 to 24 months old were subjected to cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). Human ghrelin plus GH or vehicle (normal saline) was administered subcutaneously at 5 h after CLP. At 20 h after CLP, blood and tissue samples were collected for various analyses. Combined treatment attenuated serum levels of lactate, lactate dehydrogenase, creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in aged septic rats. The integrity of the microscopic structure in the lungs, liver and kidneys was well preserved after treatment. Expression of IL-6, TNF-α, macrophage inflammatory protein-2 and keratinocyte-derived chemokine as well as myeloperoxidase activity and caspase-3 activation were significantly reduced in the lungs and liver of treated rats. Moreover, treated rats showed an improvement in cardiovascular function and increased expression of ghrelin receptor and c-fos in the brainstem. Finally, the 10-d survival of aged septic rats was increased from 29% to 64% after combined treatment and was associated with less body weight loss. Our findings warrant the development of combined human ghrelin and GH for sepsis treatment in the geriatric population.
Conflict of interest statement
P Wang is an inventor of the United States Patent No. US 8,324,151 B2: —Treatment of sepsis and septic shock using ghrelin and growth hormone.” TheraSource LLC holds the exclusive option to license the technology from the Feinstein Institute for Medical Research. P Wang is a cofounder of TheraSource LLC.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Correction of immunosuppression in aged septic rats by human ghrelin and growth hormone through the vagus nerve-dependent inhibition of TGF-β production.Mol Med. 2020 Jul 16;26(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s10020-020-00195-x. Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32677895 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effect of human ghrelin and growth hormone: Attenuation of immunosuppression in septic aged rats.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017 Oct;1863(10 Pt B):2584-2593. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.01.014. Epub 2017 Jan 20. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017. PMID: 28115288 Free PMC article.
-
Human ghrelin ameliorates organ injury and improves survival after radiation injury combined with severe sepsis.Mol Med. 2009 Nov-Dec;15(11-12):407-14. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2009.00100. Epub 2009 Sep 18. Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19779631 Free PMC article.
-
PYR-41, A Ubiquitin-Activating Enzyme E1 Inhibitor, Attenuates Lung Injury in Sepsis.Shock. 2018 Apr;49(4):442-450. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000931. Shock. 2018. PMID: 28661933 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of the inhibitory effect of ghrelin in sepsis.Hepat Med. 2010 Feb 23;2:33-8. doi: 10.2147/hmer.s7187. Hepat Med. 2010. PMID: 24367207 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Correction of immunosuppression in aged septic rats by human ghrelin and growth hormone through the vagus nerve-dependent inhibition of TGF-β production.Mol Med. 2020 Jul 16;26(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s10020-020-00195-x. Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32677895 Free PMC article.
-
Shikonin induces apoptosis of lung cancer cells via activation of FOXO3a/EGR1/SIRT1 signaling antagonized by p300.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Nov;1863(11):2584-2593. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.07.005. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27452907
-
The protective role of human ghrelin in sepsis: Restoration of CD4 T cell proliferation.PLoS One. 2018 Jul 27;13(7):e0201139. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201139. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30052667 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor Antagonist Rimonabant Decreases Levels of Markers of Organ Dysfunction and Alters Vascular Reactivity in Aortic Vessels in Late Sepsis in Rats.Inflammation. 2019 Apr;42(2):618-627. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0919-z. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 30556096
-
Ghrelin improves small intestinal barrier damage in sepsis by promoting miR-143/ATG2B-mediated autophagy.PLoS One. 2025 Aug 7;20(8):e0329488. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0329488. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40773487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang HJ, Lynm C, Glass RM. JAMA patient page Sepsis. JAMA. 2010;304:1856. - PubMed
-
- Angus DC, et al. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1303–10. - PubMed
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Moss M. The effect of age on the development and outcome of adult sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:15–21. - PubMed
-
- Kojima M, et al. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature. 1999;402:656–60. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

