Irinotecan Delivery by Lipid-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Shows Improved Efficacy and Safety over Liposomes for Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 26835979
- PMCID: PMC4851343
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.5b07781
Irinotecan Delivery by Lipid-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Shows Improved Efficacy and Safety over Liposomes for Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
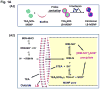
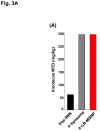
Urgent intervention is required to improve the 5 year survival rate of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). While the four-drug regimen, FOLFIRINOX (comprising irinotecan, 5-fluorouracil, oxaliplatin, and leucovorin), has a better survival outcome than the more frequently used gemcitabine, the former treatment platform is highly toxic and restricted for use in patients with good performance status. Since irinotecan contributes significantly to FOLFIRINOX toxicity (bone marrow and gastrointestinal tract), our aim was to reduce the toxicity of this drug by a custom-designed mesoporous silica nanoparticle (MSNP) platform, which uses a proton gradient for high-dose irinotecan loading across a coated lipid bilayer (LB). The improved stability of the LB-coated MSNP (LB-MSNP) carrier allowed less drug leakage systemically with increased drug concentrations at the tumor sites of an orthotopic Kras-derived PDAC model compared to liposomes. The LB-MSNP nanocarrier was also more efficient for treating tumor metastases. Equally important, the reduced leakage and slower rate of drug release by the LB-MSNP carrier dramatically reduced the rate of bone marrow, gastrointestinal, and liver toxicity compared to the liposomal carrier. We propose that the combination of high efficacy and reduced toxicity by the LB-MSNP carrier could facilitate the use of irinotecan as a first-line therapeutic to improve PDAC survival.
Keywords: FOLFIRINOX; irinotecan; lipid bilayer; mesoporous silica nanoparticle; pancreatic cancer; proton gradient; toxicity reduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures















Similar articles
-
Use of a lipid-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticle platform for synergistic gemcitabine and paclitaxel delivery to human pancreatic cancer in mice.ACS Nano. 2015;9(4):3540-57. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b00510. Epub 2015 Mar 31. ACS Nano. 2015. PMID: 25776964 Free PMC article.
-
Improved Efficacy and Reduced Toxicity Using a Custom-Designed Irinotecan-Delivering Silicasome for Orthotopic Colon Cancer.ACS Nano. 2019 Jan 22;13(1):38-53. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b06164. Epub 2018 Dec 11. ACS Nano. 2019. PMID: 30525443 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid-based mesoporous silica nanoparticles: a paradigm shift in management of pancreatic cancer.Pharm Pat Anal. 2023 Nov;12(6):261-273. doi: 10.4155/ppa-2023-0024. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Pharm Pat Anal. 2023. PMID: 38214201
-
Nanoliposomal irinotecan plus fluorouracil and folinic acid: a new treatment option in metastatic pancreatic cancer.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2016 May;16(5):485-92. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2016.1174581. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 27043737 Review.
-
Irinotecan (Campto) in the treatment of pancreatic cancer.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2003 Oct;3(5):587-93. doi: 10.1586/14737140.3.5.587. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2003. PMID: 14599083 Review.
Cited by
-
The availability of drug by liposomal drug delivery : Individual kinetics and tissue distribution of encapsulated and released drug in mice after administration of PEGylated liposomal prednisolone phosphate.Invest New Drugs. 2019 Oct;37(5):890-901. doi: 10.1007/s10637-018-0708-4. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Invest New Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30547315 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomaterial-Based Vaccine Adjuvants.J Mater Chem B. 2016 Sep 7;4(33):5496-5509. doi: 10.1039/C6TB01131D. Epub 2016 Jul 15. J Mater Chem B. 2016. PMID: 30774955 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Pancreatic Cancer Treatment by Nano-Based Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Sep 21;15(9):2363. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092363. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37765331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reverse engineering of Onivyde® - Irinotecan liposome injection.Int J Pharm. 2025 Jan 25;669:125000. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.125000. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Int J Pharm. 2025. PMID: 39608586 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Facile and Versatile Platinum Drug Delivering Silicasome Nanocarriers for Efficient Pancreatic Cancer Chemo-Immunotherapy.Small. 2021 Apr;17(14):e2005993. doi: 10.1002/smll.202005993. Epub 2021 Mar 7. Small. 2021. PMID: 33682329 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2014. CA-Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouché O, Guimbaud R, Bécouarn Y, Adenis A, Raoul JL, Gourgou-Bourgade S, de la Fouchardière C, Bennouna J, Bachet JB, Khemissa-Akouz F, Péré-Vergé D, Delbaldo C, Assenat E, Chauffert B, Michel P, Montoto-Grillot C, Ducreux M. FOLFIRINOX versus Gemcitabine for Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. New Engl J Med. 2011;364:1817–1825. - PubMed
-
- Ueno H, Okusaka T, Funakoshi A, Ishii H, Yamao K, Ishikawa O, Ohkawa S, Saitoh S. A Phase II Study of Weekly Irinotecan as First-Line Therapy for Patients with Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Chemoth Pharm. 2007;59:447–454. - PubMed
-
- Chou TH, Chen SC, Chu IM. Effect of Composition on the Stability of Liposomal Irinotecan Prepared by a pH Gradient Method. J Biosci Bioeng. 2003;95:405–408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

