Nucleophosmin integrates within the nucleolus via multi-modal interactions with proteins displaying R-rich linear motifs and rRNA
- PMID: 26836305
- PMCID: PMC4786410
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.13571
Nucleophosmin integrates within the nucleolus via multi-modal interactions with proteins displaying R-rich linear motifs and rRNA
Abstract
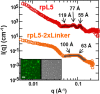
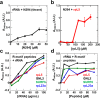
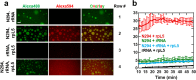
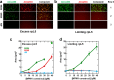
The nucleolus is a membrane-less organelle formed through liquid-liquid phase separation of its components from the surrounding nucleoplasm. Here, we show that nucleophosmin (NPM1) integrates within the nucleolus via a multi-modal mechanism involving multivalent interactions with proteins containing arginine-rich linear motifs (R-motifs) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Importantly, these R-motifs are found in canonical nucleolar localization signals. Based on a novel combination of biophysical approaches, we propose a model for the molecular organization within liquid-like droplets formed by the N-terminal domain of NPM1 and R-motif peptides, thus providing insights into the structural organization of the nucleolus. We identify multivalency of acidic tracts and folded nucleic acid binding domains, mediated by N-terminal domain oligomerization, as structural features required for phase separation of NPM1 with other nucleolar components in vitro and for localization within mammalian nucleoli. We propose that one mechanism of nucleolar localization involves phase separation of proteins within the nucleolus.
Keywords: NPM1/B23/nucleophosmin; biophysics; human; intrinsically disordered proteins; nucleolar localization; nucleolus; phase separation; single molecule fluorescence; structural biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures





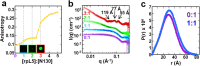
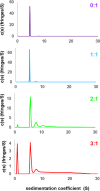
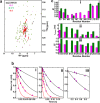

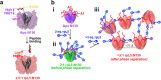



References
-
- Abragam A. Principles of Nuclear Magnetism. New York, NY: Oxford; 1961.
-
- Arai M, Ferreon JC, Wright PE. Quantitative analysis of multisite protein-ligand interactions by NMR: binding of intrinsically disordered p53 transactivation subdomains with the TAZ2 domain of CBP. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 2012;134:3792–3803. doi: 10.1021/ja209936u. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arnold O, Bilheux JC, Borreguero JM, Buts A, Campbell SI, Chapon L, Doucet M, Draper N, Ferraz Leal R, Gigg MA, Lynch VE, Markvardsen A, Mikkelson DJ, Mikkelson RL, Miller R, Palmen K, Parker P, Passos G, Perring TG, Peterson PF, Ren S, Reuter MA, Savici AT, Taylor JW, Taylor RJ, Tolchenov R, Zhou W, Zikovsky J, Campbell SI, Chapon L, Doucet M, Draper N, Ferraz Leal R, Gigg M. Mantid—data analysis and visualization package for neutron scattering and μ SR experiments. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment. 2014;764:156–166. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2014.07.029. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

