Nonlinear Imputation of Pao2/Fio2 From Spo2/Fio2 Among Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- PMID: 26836924
- PMCID: PMC4980543
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chest.2016.01.003
Nonlinear Imputation of Pao2/Fio2 From Spo2/Fio2 Among Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Abstract
Background: ARDS is an important clinical problem. The definition of ARDS requires testing of arterial blood gas to define the ratio of Pao2 to Fio2 (Pao2/Fio2 ratio). However, many patients with ARDS do not undergo blood gas measurement, which may result in underdiagnosis of the condition. As a consequence, a method for estimating Pao2 on the basis of noninvasive measurements is desirable.
Methods: Using data from three ARDS Network studies, we analyzed the enrollment arterial blood gas measurements to compare nonlinear with linear and log-linear imputation methods of estimating Pao2 from percent saturation of hemoglobin with oxygen as measured by pulse oximetry (Spo2). We compared mortality on the basis of various measured and imputed Pao2/Fio2 ratio cutoffs to ensure clinical equivalence.
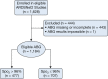
Results: We studied 1,184 patients, in 707 of whom the Spo2 ≤ 96%. Nonlinear imputation from the Spo2/Fio2 ratio resulted in lower error than linear or log-linear imputation (P < .001) for patients with Spo2 ≤ 96% but was equivalent to log-linear imputation in all patients. Ninety-day hospital mortality was 26% to 30%, depending on the Pao2/Fio2 ratio, whether nonlinearly imputed or measured. On multivariate regression, the association between imputed and measured Pao2 varied by use of vasopressors and Spo2.
Conclusions: A nonlinear equation more accurately imputes Pao2/Fio2 from Spo2/Fio2 than linear or log-linear equations, with similar observed hospital mortality depending on Spo2/Fio2 ratio vs measured Pao2/Fio2 ratios. While further refinement through prospective validation is indicated, a nonlinear imputation appears superior to prior approaches to imputation.
Keywords: acute respiratory distress syndrome; pulse oximetry; respiratory failure; severity scores.
Copyright © 2016 American College of Chest Physicians. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
16 Years and Counting? Time to Implement Noninvasive Screening for ARDS.Chest. 2016 Aug;150(2):266-7. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2016.03.023. Chest. 2016. PMID: 27502976 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rubenfeld G.D., Caldwell E., Peabody E. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(16):1685–1693. - PubMed
-
- ARDS Definition Task Force. Ranieri V.M., Rubenfeld G.D. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin Definition. JAMA. 2012;307(23):2526–2533. - PubMed
-
- Vincent J.L., Moreno R., Takala J. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. Intensive Care Med. 1996;22(7):707–710. - PubMed
-
- Garland A., Connors A.F., Jr. Indwelling arterial catheters in the intensive care unit: necessary and beneficial, or a harmful crutch? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;182(2):133–134. - PubMed
-
- Garland A. Arterial lines in the ICU: a call for rigorous controlled trials. Chest. 2014;146(5):1155–1158. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 HL123018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL123031/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 GM094465/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL123020/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL122989/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL123009/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL123433/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL123004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL123008/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL123022/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL123023/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL123027/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL122998/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL123033/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL123010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

