Subclinical Hypothyroidism in Pregnancy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 26837268
- PMCID: PMC4827301
- DOI: 10.1089/thy.2015.0418
Subclinical Hypothyroidism in Pregnancy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: The impact of subclinical hypothyroidism (SCH) and of levothyroxine replacement in pregnant women with SCH is unclear. The aims of this study were to assess (i) the impact of SCH during pregnancy on maternal and neonatal outcomes, and (ii) the effect of levothyroxine replacement therapy in these patients.
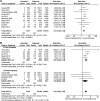
Methods: Ovid MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations, Ovid MEDLINE, the Cochrane Controlled Trials Register, Ovid EMBASE, Web of Science, and Scopus were searched from inception to January 2015. Randomized trials and cohort studies of pregnant women with SCH that examined adverse pregnancy and neonatal outcomes were included. Reviewers extracted data and assessed methodological quality in duplicate. Eighteen cohort studies at low-to-moderate risk of bias were included. Compared with euthyroid pregnant women, pregnant women with SCH were at higher risk for pregnancy loss (relative risk [RR] 2.01 [confidence interval (CI) 1.66-2.44]), placental abruption (RR 2.14 [CI 1.23-3.70]), premature rupture of membranes (RR 1.43 [CI 1.04-1.95]), and neonatal death (RR 2.58 [CI 1.41-4.73]). One study at high risk of bias compared pregnant women with SCH who received levothyroxine to those who did not and found no significant decrease in the rate of pregnancy loss, preterm delivery, gestational hypertension, low birth weight, or low Apgar score.
Conclusions: SCH during pregnancy is associated with multiple adverse maternal and neonatal outcomes. The value of levothyroxine therapy in preventing these adverse outcomes remains uncertain.
Figures
References
-
- Allan WC, Haddow JE, Palomaki GE, Williams JR, Mitchell ML, Hermos RJ, Faix JD, Klein RZ. 2000. Maternal thyroid deficiency and pregnancy complications: Implications for population screening. J Med Screen 7:127–130 - PubMed
-
- Stagnaro-Green A, Abalovich M, Alexander E, Azizi F, Mestman J, Negro R, Nixon A, Pearce EN, Soldin OP, Sullivan S, Wiersinga W. 2011. Guidelines of the American Thyroid Association for the diagnosis and management of thyroid disease during pregnancy and postpartum. Thyroid 21:1081–1125 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blatt AJ, Nakamoto JM, Kaufman HW. 2012. National status of testing for hypothyroidism during pregnancy and postpartum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:777–784 - PubMed
-
- Negro R, Stagnaro-Green A. 2014. Diagnosis and management of subclinical hypothyroidism in pregnancy. BMJ 349:g4929. - PubMed
-
- Casey BM, Dashe JS, Wells CE, McIntire DD, Byrd W, Leveno KJ, Cunningham FG. 2005. Subclinical hypothyroidism and pregnancy outcomes. Obstet Gynecol 105:239–245 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

