miR-320a mediates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by targeting VEGF signal pathway
- PMID: 26837315
- PMCID: PMC4761722
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.100876
miR-320a mediates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by targeting VEGF signal pathway
Erratum in
-
Correction for: miR-320a mediates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by targeting VEGF signal pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jun 30;13(12):16895-16896. doi: 10.18632/aging.203263. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34191749 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Vascular homeostasis abnormalities may involve in doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity.
Methods: Enhanced cardiac miR-320a expression, reduced cardiac microvessel density and impaired cardiac function were observed in mice treated by anthracycline doxorubicin. To further explore the role of miR-320a in doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity, microRNA mimics/inhibitor in vitro and rAAV administration in vivo were employed in mice.
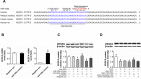
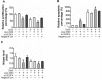
Results: Knockdown of miR-320a not only resulted in enhanced proliferation and inhibited apoptosis in cultured endothelial cells, but also attenuated cardiac abnormalities induced by doxorubicin. On the contrary, overexpression of miR-320a enhanced apoptosis in vitro, and aggravated vessel abnormalities in heart and subsequent cardiac dysfunction in mice. Furthermore, Western blot assays showed that VEGF-A was a potential target of miR-320a, which was verified by anti-Ago2 co-immunoprecipitation. Moreover, as same as miR-320a, siRNA against VEGF-A reinforced doxorubicin induced endothelial cells injury. Finally, the negative effects of miR-320a on vascular homeostasis and cardiac function were alleviated by VEGF-A re-expression in doxorubicin treated mice.
Conclusion: Our observations demonstrate that miR-320a play important roles in doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity via vessel homeostasis in heart and thus, inhibition of miR-320a may be applied to the treatment of cardiac dysfunction induced by anthracycline.
Keywords: VEGF-A; cardiotoxicity; doxorubicin; miR-320a; vascular homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures












Similar articles
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Doxorubicin-Induced Vascular Remodeling.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 12;25(24):13335. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413335. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-526b-3p mediates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by targeting STAT3 to inactivate VEGFA.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Mar;123:109751. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109751. Epub 2020 Jan 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31958751
-
Regulatory role of microRNA-320a in the proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of trophoblasts and endothelial cells by targeting estrogen-related receptor γ.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Jan;234(1):682-691. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26842. Epub 2018 Sep 14. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30216440
-
MiR-200a-3p Aggravates DOX-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Targeting PEG3 Through SIRT1/NF-κB Signal Pathway.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2021 Apr;21(4):302-313. doi: 10.1007/s12012-020-09620-3. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33638775
-
The effects of doxorubicin on cardiac calcium homeostasis and contractile function.J Cardiol. 2022 Aug;80(2):125-132. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2022.01.001. Epub 2022 Jan 24. J Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35086744 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential expression of epigenetic modifiers in early and late cardiotoxic heart failure reveals DNA methylation as a key regulator of cardiotoxicity.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Mar 9;10:884174. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.884174. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 36970338 Free PMC article.
-
An integrative review of nonobvious puzzles of cellular and molecular cardiooncology.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023 May 23;28(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00451-y. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37221467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Doxorubicin-Induced Vascular Remodeling.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 12;25(24):13335. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413335. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Positive feedback loop of miR-320 and CD36 regulates the hyperglycemic memory-induced diabetic diastolic cardiac dysfunction.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022 Dec 14;31:122-138. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.12.009. eCollection 2023 Mar 14. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022. PMID: 36618264 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs in cancer therapy-induced cardiotoxicity: Mechanisms, biomarkers, and treatments.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 23;9:946137. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.946137. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36082126 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Carvalho FS, Burgeiro A, Garcia R, Moreno AJ, Carvalho RA, Oliveira PJ. Doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: from bioenergetic failure and cell death to cardiomyopathy. Med Res Rev. 2014;34:106–135. - PubMed
-
- Yeh ET, Bickford CL. Cardiovascular complications of cancer therapy: incidence, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2009;53:2231–2247. - PubMed
-
- Cardinale D, Colombo A, Bacchiani G, Tedeschi I, Meroni CA, Veglia F, Civelli M, Lamantia G, Colombo N, Curigliano G, Fiorentini C, Cipolla CM. Early detection of anthracycline cardiotoxicity and improvement with heart failure therapy. Circulation. 2015;131:1981–1988. - PubMed
-
- Vejpongsa P, Yeh ET. Prevention of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: challenges and opportunities. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2014;64:938–945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

