MicroRNA-195a-5p inhibits mouse medullary thymic epithelial cells proliferation by directly targeting Smad7
- PMID: 26837421
- PMCID: PMC4885129
- DOI: 10.1093/abbs/gmv136
MicroRNA-195a-5p inhibits mouse medullary thymic epithelial cells proliferation by directly targeting Smad7
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: Microrna-195a-5p inhibits mouse medullary thymic epithelial cells proliferation by directly targeting Smad7.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021 Dec 8;53(12):1741. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmab087. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021. PMID: 34136899 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
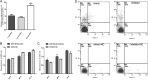
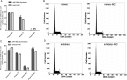
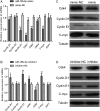
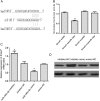
MiR-195 has been implicated in inhibiting cell proliferation in different types of tumors. Whether it contributes to the process of thymic epithelial cells (TECs) proliferation remains unclear. In this study, we found that miR-195a-5p was highly up-regulated in the TECs isolated from the aging mice. Further experiments showed that miR-195a-5p mimic transfection inhibited the proliferation of mouse medullary thymic epithelial cell line 1 (MTEC1), whereas the transfection of miR-195a-5p inhibitor in MTEC1 had the opposite effect. In addition, miR-195a-5p had no obvious effect on MTEC1 apoptosis. Furthermore, Smad7, a negative regulator of transforming growth factor β pathway, was confirmed as a direct target of miR-195a-5p by luciferase assays. Taken together, our results indicate that miR-195a-5p inhibits MTEC1 proliferation, at least in part, via down-regulation of Smad7.
Keywords: cell proliferation, Smad7; miR-195a-5p; mouse thymic epithelial cell.
Published by Oxford University Press ABBS Editorial Office in association with Oxford University Press on behalf of the Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences 2016. This work is written by (a) US Government employee(s) and is in the public domain in the US.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-152-3p Represses the Proliferation of the Thymic Epithelial Cells by Targeting Smad2.Genes (Basel). 2022 Mar 24;13(4):576. doi: 10.3390/genes13040576. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35456382 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-181a-5p enhances cell proliferation in medullary thymic epithelial cells via regulating TGF-β signaling.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2016 Sep;48(9):840-9. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmw068. Epub 2016 Jul 13. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2016. PMID: 27411504
-
miR-199b-5p enhances the proliferation of medullary thymic epithelial cells via regulating Wnt signaling by targeting Fzd6.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021 Jan 12;53(1):36-45. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmaa145. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021. PMID: 33313638
-
MicroRNA-195a-5p Regulates Blood Pressure by Inhibiting NKCC2A.Hypertension. 2023 Feb;80(2):426-439. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.122.19794. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Hypertension. 2023. PMID: 36448465 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage-derived exosomal miR-195a-5p impairs tubular epithelial cells mitochondria in acute kidney injury mice.FASEB J. 2023 Jan;37(1):e22691. doi: 10.1096/fj.202200644R. FASEB J. 2023. PMID: 36515680
Cited by
-
Effects of PAMK on lncRNA, miRNA, and mRNA expression profiles of thymic epithelial cells.Funct Integr Genomics. 2022 Oct;22(5):849-863. doi: 10.1007/s10142-022-00863-7. Epub 2022 May 4. Funct Integr Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35505120
-
MicroRNA-195 regulates proliferation, migration, angiogenesis and autophagy of endothelial progenitor cells by targeting GABARAPL1.Biosci Rep. 2016 Oct 14;36(5):e00396. doi: 10.1042/BSR20160139. Print 2016 Oct. Biosci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27623937 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis reveals a potential regulatory mechanism of the lnc-5423.6/IGFBP5 axis in the early stages of mouse thymic involution.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2023 Apr 19;55(4):548-560. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2023042. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2023. PMID: 37078747 Free PMC article.
-
miR-152-3p Represses the Proliferation of the Thymic Epithelial Cells by Targeting Smad2.Genes (Basel). 2022 Mar 24;13(4):576. doi: 10.3390/genes13040576. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35456382 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of circRNA expression profiles and circRNA-associated competing endogenous RNA networks in the development of mouse thymus.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jun;24(11):6340-6349. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15276. Epub 2020 Apr 19. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32307889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takahama Y, Takada K, Murata S, Tanaka K. β5t-containing thymoproteasome: specific expression in thymic cortical epithelial cells and role in positive selection of CD8+ T cells. Curr Opin Immunol 2012, 24: 92–98. - PubMed
-
- Anderson G, Lane PJ, Jenkinson EJ. Generating intrathymic microenvironments to establish T-cell tolerance. Nat Rev Immunol 2007, 7: 954–963. - PubMed
-
- Aw D, Silva AB, Maddick M, von Zglinicki T, Palmer DB. Architectural changes in the thymus of aging mice. Aging Cell 2008, 7: 158–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

