Defining Swallowing-Related Quality of Life Profiles in Individuals with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- PMID: 26837611
- PMCID: PMC4871719
- DOI: 10.1007/s00455-015-9686-2
Defining Swallowing-Related Quality of Life Profiles in Individuals with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Abstract
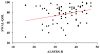
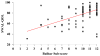
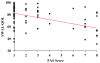
Although it is known that dysphagia contributes to significant malnutrition, pneumonia, and mortality in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), it remains unclear how swallowing impairment impacts quality of life in this vulnerable patient population. The aim of the current study was to (1) delineate swallow-related quality of life (SR-QOL) profiles in individuals with ALS and (2) evaluate relationships between SR-QOL, degree of swallowing impairment, and ALS global disease progression. Eighty-one ALS patients underwent a standardized videofluoroscopic swallow study and completed the swallowing quality of life (SWAL-QOL) instrument and ALS functional rating scale-revised (ALSFRS-R). Penetration Aspiration Scale (PAS) scores were derived by a blinded rater. Correlation analyses and a between groups ANOVA (safe vs. penetrators vs. aspirators) were performed. Mean SWAL-QOL score for this cohort was 75.94 indicating a moderate degree of SR-QOL impairment with fatigue, eating duration, and communication representing the most affected domains. Correlations were revealed between the SWAL-QOL and (1) PAS (r = -0.39, p < 0.001) and (2) ALSFRS-R (r = 0.23, p < 0.05). Mean (SD) SWAL-QOL scores for safe versus penetrator versus aspirator groups were 81.2 (2.3) versus 77 (3.4) versus 58.7 (5.9), respectively, with a main effect observed [F(2,78) = 9.71, p < 0.001]. Post hoc testing revealed lower SWAL-QOL scores for aspirators versus safe swallowers (p < 0.001) and aspirators versus penetrators (p < 0.001). Overall, SR-QOL was moderately reduced in this cohort of ALS patients and profoundly impacted in ALS aspirators and individuals with advanced disease. These findings highlight the importance of early multidisciplinary intervention to not only avoid malnutrition, weight loss, and pulmonary sequelae but also the associated reduced QOL seen in these individuals.
Keywords: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; Deglutition; Deglutition disorders; Dysphagia; Quality of life.
Figures
References
-
- Brooks BR, Miller RG, Swash M, Munsat TL. El Escorial revisited: revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord. 2000;1(5):293–9. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter RJ, 3rd, McDonald TJ, Howard FM., Jr The otolaryngologic presentation of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Otolaryngology. 1978;86(3 Pt 1):ORL479–84. - PubMed
-
- Miller RG, Jackson CE, Kasarskis EJ, England JD, Forshew D, Johnston W, Kalra S, Katz JS, Mitsumoto H, Rosenfeld J, Shoesmith C, Strong MJ, Woolley SC. Practice parameter update: the care of the patient with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: multi-disciplinary care, symptom management, and cognitive/behavioral impairment (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2009;73(15):1227–33. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181bc01a4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

