Improving Engagement in the HIV Care Cascade: A Systematic Review of Interventions Involving People Living with HIV/AIDS as Peers
- PMID: 26837630
- PMCID: PMC4970970
- DOI: 10.1007/s10461-016-1307-z
Improving Engagement in the HIV Care Cascade: A Systematic Review of Interventions Involving People Living with HIV/AIDS as Peers
Abstract
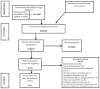
Improving patient engagement in HIV care is critical for maximizing the impact of antiretroviral therapy (ART). We conducted a systematic review of studies that used HIV-positive peers to bolster linkage, retention, and/or adherence to ART. We searched articles published and indexed in Pubmed, PsycINFO, and CINAHL between 1996 and 2014. Peers were required to be HIV-positive. Studies were restricted to those published in English. Nine studies with n = 4658 participants met the inclusion criteria. Peer-based interventions were predominantly focused on improving adherence to ART, or evaluations of retention and adherence via viral suppression. Five (56 %) were conducted in sub-Saharan Africa. Overall findings were mixed on the impact of peers on ART adherence, viral suppression, and mortality. While positive effects of peer interventions on improving linkage and retention were found, there were limited studies assessing these outcomes. Additional research is warranted to demonstrate the impact of peers on linkage and retention in diverse populations.
Keywords: Antiretroviral adhernce; Linkage to HIV care; Peer interventions; Retention in HIV care; Sub-Saharan Africa; Systematic review.
Figures
References
-
- Thompson MA, Mugavero MJ, Amico KR, et al. Guidelines for improving entry into and retention in care and antiretroviral adherence for persons with HIV: evidence-based recommendations from an International Association of Physicians in AIDS Care panel. Ann Intern Med. 2012;156(11):817–33. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous