PPARα-dependent cholesterol/testosterone disruption in Leydig cells mediates 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-induced testicular toxicity in mice
- PMID: 26838045
- PMCID: PMC6334304
- DOI: 10.1007/s00204-016-1669-z
PPARα-dependent cholesterol/testosterone disruption in Leydig cells mediates 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-induced testicular toxicity in mice
Abstract
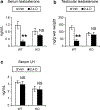
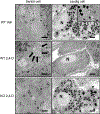
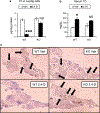
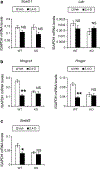
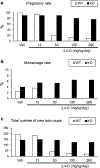
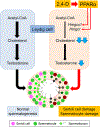
It was reported that 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), a commonly used herbicide and a possible endocrine disruptor, can disturb spermatogenesis, but the precise mechanism is not understood. Since 2,4-D is a weak peroxisome proliferator in hepatocytes and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) is also expressed in Leydig cells, this study aimed to investigate the link between PPARα and 2,4-D-mediated testicular dysfunction. 2,4-D (130 mg/kg/day) was administered to wild-type and Ppara-null mice for 2 weeks, and the alterations in testis and testosterone/cholesterol metabolism in Leydig cells were examined. Treatment with 2,4-D markedly decreased testicular testosterone in wild-type mice, leading to degeneration of spermatocytes and Sertoli cells. The 2,4-D decreased cholesterol levels in Leydig cells of wild-type mice through down-regulating the expression of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A synthase 1 and reductase, involved in de novo cholesterogenesis. However, the mRNAs encoding the important proteins involved in testosterone synthesis were unchanged by 2,4-D except for CYP17A1, indicating that exhausted cholesterol levels in the cells is a main reason for reduced testicular testosterone. Additionally, pregnancy rate and the number of pups between 2,4-D-treated wild-type male mice and untreated female mice were significantly lower compared with those between untreated couples. These phenomena were not observed in 2,4-D-treated Ppara-null males. Collectively, these results suggest a critical role for PPARα in 2,4-D-induced testicular toxicity due to disruption of cholesterol/testosterone homeostasis in Leydig cells. This study yields novel insights into the possible mechanism of testicular dysfunction and male infertility caused by 2,4-D.
Keywords: 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid; Cholesterol; Leydig cell; PPARα; Testicular toxicity; Testosterone.
Figures


References
-
- Abdellatif AG, Préat V, Vamecq J, Nilsson R, Roberfroid M (1990) Peroxisome proliferation and modulation of rat liver carcinogenesis by 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid, perfluorooctanoic acid and nafenopin. Carcinogenesis 11:1899–1902 - PubMed
-
- Amer SM, Aly FA (2001) Genotoxic effect of 2,4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid and its metabolite 2,4-dichlorophenol in mouse. Mutat Res 494:1–12 - PubMed
-
- Aoyama T, Yamano S, Waxman DJ, Lapenson DP, Meyer UA, Fischer V, Tyndale R, Inaba T, Kalow W, Gelboin HV et al. (1989) Cytochrome P-450 hPCN3, a novel cytochrome P-450 IIIA gene product that is differentially expressed in adult human liver. cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence and distinct specificities of cDNA-expressed hPCN1 and hPCN3 for the metabolism of steroid hormones and cyclosporine. J Biol Chem 264:10388–10395 - PubMed
-
- Aoyama T, Peters JM, Iritani N, Nakajima T, Furihata K, Hashimoto T, Gonzalez FJ (1998) Altered constitutive expression of fatty acid-metabolizing enzymes in mice lacking the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha). J Biol Chem 273:5678–5684 - PubMed
-
- Biegel LB, Hurtt ME, Frame SR, O’Connor JC, Cook JC (2001) Mechanisms of extrahepatic tumor induction by peroxisome proliferators in male CD rats. Toxicol Sci 60:44–55 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

