Clinicopathological Significance of Osteopontin in Cholangiocarcinoma Cases
- PMID: 26838210
- PMCID: PMC4955515
- DOI: 10.7314/apjcp.2016.17.1.201
Clinicopathological Significance of Osteopontin in Cholangiocarcinoma Cases
Abstract
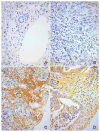
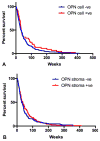
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is generally a rare primary liver tumor of the bile duct with extremely poor clinical outcomes due to late diagnosis. Osteopontin (OPN) is the most abundant expressed gene in intrahepatic CCA and its involvement in tumor aggressiveness suggests it could be a useful prognostic biomarker. However, the prognostic significance of OPN expression in CCA is still controversial. We therefore immunohistochemically studied OPN expression in 354 resected CCAs and correlated the results with patient clinicopathological parameters. OPN expression was separately scored according to the percentage of cancer cells or degree of stromal tissue staining and classified as low (score 0-1) and high (score 2-3). OPN expression in CCA cells was found in 177 out of 354 patients (56.5%), whereas stroma was positive in 185 out of 354 patients (52.3%). Univariate analysis with several of the aforementioned parameters revealed that stromal but not cancer cell OPN expression was significantly associated with tumor size, tumor direct invasion into normal liver parenchyma, regional lymph node metastasis and higher staging. The combination of cancer cell and stromal OPN expression demonstrated a positive trend for linkage with lymph node metastasis. Multivariate analysis identified gender, the presence of lymphatic permeation and lymph node metastasis, but not OPN expression, as independent prognostic factors. This study confirms the presence of stromal OPN expression in tumor aggressiveness but not survival in CCA patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decreased expression of osteopontin is related to tumor aggressiveness and clinical outcome of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.Liver Int. 2004 Feb;24(1):38-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2004.00886.x. Liver Int. 2004. PMID: 15101999
-
The Prognostic Role of SOCS3 and A20 in Human Cholangiocarcinoma.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 20;10(10):e0141165. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141165. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26485275 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Smad7 in cholangiocarcinoma: prognostic significance and implications for tumor metastasis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(10):5161-5. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2012.13.10.5161. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012. PMID: 23244128
-
Synchronous double cancers of primary hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a case report and review of the literature.World J Surg Oncol. 2014 Nov 10;12:337. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-12-337. World J Surg Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25385169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel approaches in search for biomarkers of cholangiocarcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Apr 21;28(15):1508-1525. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i15.1508. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35582128 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Tumor Microenvironment in Cholangiocarcinoma Progression.Hepatology. 2021 Jan;73 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):75-85. doi: 10.1002/hep.31410. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Hepatology. 2021. PMID: 32500550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteopontin: an indispensable component in common liver, pancreatic, and biliary related disease.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Nov 22;150(12):508. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-06038-0. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39572438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteopontin Takes Center Stage in Chronic Liver Disease.Hepatology. 2021 Apr;73(4):1594-1608. doi: 10.1002/hep.31582. Hepatology. 2021. PMID: 32986864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Landscape of NcRNAs involved in drug resistance of breast cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2023 Jul;25(7):1869-1892. doi: 10.1007/s12094-023-03189-3. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37067729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers and Genetic Markers of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Cholangiocarcinoma-What Do We Already Know.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 15;14(6):1493. doi: 10.3390/cancers14061493. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326644 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bourguignon LY, Zhu H, Shao L, et al. Rhokinase (ROK) promotes CD44v(3,8-10)-ankyrin interaction and tumor cell migration in metastatic breast cancer cells. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1999;43:269–87. - PubMed
-
- Fedor HL, De Marzo AM. Practical methods for tissue microarray construction. Methods Mol Med. 2005;103:89–101. - PubMed
-
- Grunnet M, Mau-Sorensen M. Serum tumor markers in bile duct cancer--a review. Biomarkers. 2014;19:437–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

