Exercise and fall prevention self-management to reduce mobility-related disability and falls after fall-related lower limb fracture in older people: protocol for the RESTORE (Recovery Exercises and STepping On afteR fracturE) randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 26838998
- PMCID: PMC4739405
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-016-0206-5
Exercise and fall prevention self-management to reduce mobility-related disability and falls after fall-related lower limb fracture in older people: protocol for the RESTORE (Recovery Exercises and STepping On afteR fracturE) randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Lasting disability and further falls are common and costly problems in older people following fall-related lower limb and pelvic fractures. Exercise interventions can improve mobility after fracture and reduce falls in older people, however the optimal approach to rehabilitation after fall-related lower limb and pelvic fracture is unclear. This randomised controlled trial aims to evaluate the effects of an exercise and fall prevention self-management intervention on mobility-related disability and falls in older people following fall-related lower limb or pelvic fracture. Cost-effectiveness of the intervention will also be investigated.
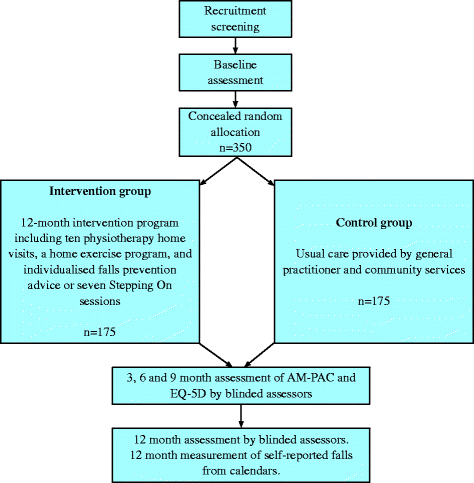
Methods/design: A randomised controlled trial with concealed allocation, assessor blinding for physical performance tests and intention-to-treat analysis will be conducted. Three hundred and fifty people aged 60 years and over with a fall-related lower limb or pelvic fracture, who are living at home or in a low care residential aged care facility and have completed active rehabilitation, will be recruited. Participants will be randomised to receive a 12-month intervention or usual care. The intervention group will receive ten home visits from a physiotherapist to prescribe an individualised exercise program with motivational interviewing, plus fall prevention education through individualised advice from the physiotherapist or attendance at the group based "Stepping On" program (seven two-hour group sessions). Participants will be followed for a 12-month period. Primary outcome measures will be mobility-related disability and falls. Secondary outcomes will include measures of balance and mobility, falls risk, physical activity, walking aid use, frailty, pain, nutrition, falls efficacy, mood, positive and negative affect, quality of life, assistance required, hospital readmission, and health-system and community-service contact.
Discussion: This study will determine the effect and cost-effectiveness of this exercise self management intervention on mobility-related disability and falls in older people who have recently sustained a fall-related lower limb or pelvic fracture. The results will have implications for the design and implementation of interventions for older people with fall related lower limb fractures. The findings of this study will be disseminated in peer-reviewed journals and through professional and scientific conferences.
Trial registration: Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry: ACTRN12610000805077.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exercise to Reduce Mobility Disability and Prevent Falls After Fall-Related Leg or Pelvic Fracture: RESTORE Randomized Controlled Trial.J Gen Intern Med. 2020 Oct;35(10):2907-2916. doi: 10.1007/s11606-020-05666-9. Epub 2020 Feb 3. J Gen Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32016702 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Minimising disability and falls in older people through a post-hospital exercise program: a protocol for a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation.BMC Geriatr. 2009 Feb 26;9:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2318-9-8. BMC Geriatr. 2009. PMID: 19245697 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Trial Protocol: Home-based exercise programs to prevent falls and upper limb dysfunction among community-dwelling older people: study protocol for the BEST (Balance Exercise Strength Training) at Home randomised, controlled trial.J Physiother. 2018 Apr;64(2):121. doi: 10.1016/j.jphys.2017.10.001. Epub 2018 Mar 28. J Physiother. 2018. PMID: 29605522 Clinical Trial.
-
Exercise for preventing falls in older people living in the community.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jan 31;1(1):CD012424. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012424.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30703272 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise for people with a fragility fracture of the pelvis or lower limb: a systematic review of interventions evaluated in clinical trials and reporting quality.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020 Jul 4;21(1):435. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03361-8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020. PMID: 32622352 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Multifactorial and multiple component interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 23;7(7):CD012221. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012221.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30035305 Free PMC article.
-
Fracture Experiences and Long-Term Care Initiation among Older Population: Analysis of Korean National Health Insurance Service-Senior Cohort Study.Ann Geriatr Med Res. 2019 Sep;23(3):115-124. doi: 10.4235/agmr.19.0021. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Ann Geriatr Med Res. 2019. PMID: 32743299 Free PMC article.
-
Extremity injuries and dementia disproportionately increase the risk for long-term care at older age in an analysis of German Health Insurance routine data for the years 2006 to 2010.Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2016 Dec 6;13:9. doi: 10.1186/s11556-016-0169-8. eCollection 2016. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2016. PMID: 27980691 Free PMC article.
-
The bidirectional relationship between homebound status and falls among older adults: a longitudinal study.BMC Geriatr. 2022 Dec 1;22(1):923. doi: 10.1186/s12877-022-03588-1. BMC Geriatr. 2022. PMID: 36457078 Free PMC article.
-
The risk of injuries during work and its association with precipitation: New insight from a sentinel-based surveillance and a case-crossover design.Front Public Health. 2023 Mar 2;11:1117948. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1117948. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36935708 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Handoll HH, Sherrington C, Mak JC. Interventions for improving mobility after hip fracture surgery in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;3:CD001704. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical