Endothelial p110γPI3K Mediates Endothelial Regeneration and Vascular Repair After Inflammatory Vascular Injury
- PMID: 26839042
- PMCID: PMC4792690
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.020918
Endothelial p110γPI3K Mediates Endothelial Regeneration and Vascular Repair After Inflammatory Vascular Injury
Abstract
Background: The integrity of endothelial monolayer is a sine qua non for vascular homeostasis and maintenance of tissue-fluid balance. However, little is known about the signaling pathways regulating regeneration of the endothelial barrier after inflammatory vascular injury.
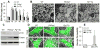
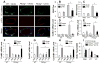
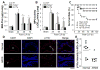
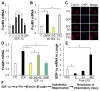
Methods and results: Using genetic and pharmacological approaches, we demonstrated that endothelial regeneration selectively requires activation of p110γPI3K signaling, which thereby mediates the expression of the endothelial reparative transcription factor Forkhead box M1 (FoxM1). We observed that FoxM1 induction in the pulmonary vasculature was inhibited in mice treated with a p110γ-selective inhibitor and in Pik3cg(-/-) mice after lipopolysaccharide challenge. Pik3cg(-/-) mice exhibited persistent lung inflammation induced by sepsis and sustained increase in vascular permeability. Restoration of expression of either p110γ or FoxM1 in pulmonary endothelial cells of Pik3cg(-/-) mice restored endothelial regeneration and normalized the defective vascular repair program. We also observed diminished expression of p110γ in pulmonary vascular endothelial cells of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, suggesting that impaired p110γ-FoxM1 vascular repair signaling pathway is a critical factor in persistent leaky lung microvessels and edema formation in the disease.
Conclusions: We identify p110γ as the critical mediator of endothelial regeneration and vascular repair after sepsis-induced inflammatory injury. Thus, activation of p110γ-FoxM1 endothelial regeneration may represent a novel strategy for the treatment of inflammatory vascular diseases.
Keywords: endothelial regeneration; endothelium, vascular; inflammation; vascular diseases; vascular repair.
© 2016 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures
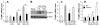
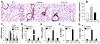

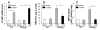
References
-
- Aird WC. Endothelium in health and disease. Pharmacol Rep. 2008;60:139–143. - PubMed
-
- Cines DB, Pollak ES, Buck CA, Loscalzo J, Zimmerman GA, McEver RP, Pober JS, Wick TM, Konkle BA, Schwartz BS, Barnathan ES, McCrae KR, Hug BA, Schmidt AM, Stern DM. Endothelial cells in physiology and in the pathophysiology of vascular disorders. Blood. 1998;91:3527–3561. - PubMed
-
- Mehta D, Malik AB. Signaling mechanisms regulating endothelial permeability. Physiol Rev. 2006;86:279–367. - PubMed
-
- Owens GK, Kumar MS, Wamhoff BR. Molecular regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation in development and disease. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:767–801. - PubMed
-
- Austin GE, Ratliff NB, Hollman J, Tabei S, Phillips DF. Intimal proliferation of smooth muscle cells as an explanation for recurrent coronary artery stenosis after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1985;6:369–375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

