c-Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK) induces phosphorylation of amyloid precursor protein (APP) at Thr668, in okadaic acid-induced neurodegeneration
- PMID: 26839154
- PMCID: PMC5032005
- DOI: 10.5483/bmbrep.2016.49.7.246
c-Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK) induces phosphorylation of amyloid precursor protein (APP) at Thr668, in okadaic acid-induced neurodegeneration
Abstract
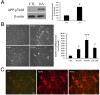
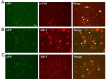
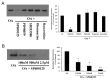
Several lines of evidence have revealed that phosphorylation of amyloid precursor protein (APP) at Thr668 is involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Okadaic acid (OA), a protein phosphatase-2A inhibitor, has been used in AD research models to increase tau phosphorylation and induce neuronal death. We previously showed that OA increased levels of APP and induced accumulation of APP in axonal swellings. In this study, we found that in OA-treated neurons, phosphorylation of APP at Thr668 increased and accumulated in axonal swellings by c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and not by Cdk5 or ERK/MAPK. These results suggest that JNK may be one of therapeutic targets for the treatment of AD. [BMB Reports 2016; 49(7): 376-381].
Figures

Similar articles
-
BACE inhibitor reduces APP-beta-C-terminal fragment accumulation in axonal swellings of okadaic acid-induced neurodegeneration.Neurobiol Dis. 2006 May;22(2):435-44. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2005.12.013. Epub 2006 Feb 9. Neurobiol Dis. 2006. PMID: 16480887
-
NGF controls APP cleavage by downregulating APP phosphorylation at Thr668: relevance for Alzheimer's disease.Aging Cell. 2016 Aug;15(4):661-72. doi: 10.1111/acel.12473. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Aging Cell. 2016. PMID: 27076121 Free PMC article.
-
c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-interacting protein-3 facilitates phosphorylation and controls localization of amyloid-beta precursor protein.J Neurosci. 2005 Apr 13;25(15):3741-51. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0152-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15829626 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired autophagy and APP processing in Alzheimer's disease: The potential role of Beclin 1 interactome.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Jul-Aug;106-107:33-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.06.002. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23827971 Review.
-
The role of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in Alzheimer's disease.Neurosignals. 2002 Sep-Oct;11(5):270-81. doi: 10.1159/000067426. Neurosignals. 2002. PMID: 12566928 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovering a novel dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A (DYRK1A) inhibitor and its impact on tau phosphorylation and amyloid-β formation.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2024 Dec;39(1):2418470. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2024.2418470. Epub 2024 Nov 4. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39494990 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanism of Vitamin K2 Protection against Amyloid-β-Induced Cytotoxicity.Biomolecules. 2021 Mar 13;11(3):423. doi: 10.3390/biom11030423. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33805625 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of 1-Pyrimidinyl-2-Aryl-4,6-Dihydropyrrolo [3,4-d]Imidazole-5(1H)-Carboxamide as a Novel JNK Inhibitor.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 2;21(5):1698. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051698. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32131443 Free PMC article.
-
The disturbance of thyroid-associated hormone and its receptors in brain and blood circulation existed in the early stage of mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Mar 7;15(5):1591-1602. doi: 10.18632/aging.204570. Epub 2023 Mar 7. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 36897166 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin Resistance Exacerbates Alzheimer Disease via Multiple Mechanisms.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jul 19;15:687157. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.687157. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34349617 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tachibana K, Scheuer PJ, Tsukitani Y, et al. Okadaic acid, a cytotoxic polyether from two marine sponges of the genus Halichondria. J Am Chem Soc. (1981);103:2469–2471. doi: 10.1021/ja00399a082. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

