Marine mammals harbor unique microbiotas shaped by and yet distinct from the sea
- PMID: 26839246
- PMCID: PMC4742810
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10516
Marine mammals harbor unique microbiotas shaped by and yet distinct from the sea
Abstract
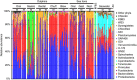
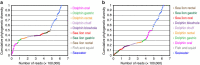
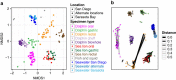
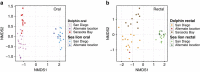
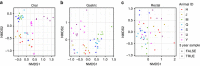
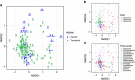
Marine mammals play crucial ecological roles in the oceans, but little is known about their microbiotas. Here we study the bacterial communities in 337 samples from 5 body sites in 48 healthy dolphins and 18 healthy sea lions, as well as those of adjacent seawater and other hosts. The bacterial taxonomic compositions are distinct from those of other mammals, dietary fish and seawater, are highly diverse and vary according to body site and host species. Dolphins harbour 30 bacterial phyla, with 25 of them in the mouth, several abundant but poorly characterized Tenericutes species in gastric fluid and a surprisingly paucity of Bacteroidetes in distal gut. About 70% of near-full length bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA sequences from dolphins are unique. Host habitat, diet and phylogeny all contribute to variation in marine mammal distal gut microbiota composition. Our findings help elucidate the factors structuring marine mammal microbiotas and may enhance monitoring of marine mammal health.
Figures


References
-
- Estes J. A. et al. Trophic downgrading of planet Earth. Science 333, 301–306 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Dierauf L. A. & Gulland F. M. D. CRC Handbook of Marine Mammal Medicine CRC Press (2001).
-
- Wells R. S. et al. Bottlenose dolphins as marine ecosystem sentinels: developing a health monitoring system. Ecohealth 1, 246–254 (2004).
-
- Evans P. G. H. & Raga J. A. Marine Mammals: Biology and Conservation Springer (2001).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

