Predictive Factors of Mortality in Population of Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH): Results from a Korean PNH Registry
- PMID: 26839475
- PMCID: PMC4729501
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.2.214
Predictive Factors of Mortality in Population of Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH): Results from a Korean PNH Registry
Abstract
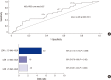
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is a progressive, systemic, life-threatening disease, characterized by chronic uncontrolled complement activation. A retrospective analysis of 301 Korean PNH patients who had not received eculizumab was performed to systematically identify the clinical symptoms and signs predictive of mortality. PNH patients with hemolysis (lactate dehydrogenase [LDH] ≥ 1.5 × the upper limit of normal [ULN]) have a 4.8-fold higher mortality rate compared with the age- and sex-matched general population (P < 0.001). In contrast, patients with LDH < 1.5 × ULN have a similar mortality rate as the general population (P = 0.824). Thromboembolism (TE) (odds ratio [OR] 7.11; 95% confidence interval [CI] (3.052-16.562), renal impairment (OR, 2.953; 95% CI, 1.116-7.818) and PNH-cytopenia (OR, 2.547; 95% CI, 1.159-5.597) are independent risk factors for mortality, with mortality rates 14-fold (P < 0.001), 8-fold (P < 0.001), and 6.2-fold (P < 0.001) greater than that of the age- and sex-matched general population, respectively. The combination of hemolysis and 1 or more of the clinical symptoms such as abdominal pain, chest pain, or dyspnea, resulted in a much greater increased mortality rate when compared with patients with just the individual symptom alone or just hemolysis. Early identification of risk factors related to mortality is crucial for the management of PNH. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as NCT01224483.
Keywords: Mortality; PNH; Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria; Risk Factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Hillmen P, Lewis SM, Bessler M, Luzzatto L, Dacie JV. Natural history of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1253–1259. - PubMed
-
- Socié G, Mary JY, de Gramont A, Rio B, Leporrier M, Rose C, Heudier P, Rochant H, Cahn JY, Gluckman E French Society of Haematology. Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria: long-term follow-up and prognostic factors. Lancet. 1996;348:573–577. - PubMed
-
- Hill A, Kelly RJ, Hillmen P. Thrombosis in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 2013;121:4985–4996. - PubMed
-
- Lee JW, Jang JH, Kim JS, Yoon SS, Lee JH, Kim YK, Jo DY, Chung J, Sohn SK. Clinical signs and symptoms associated with increased risk for thrombosis in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria from a Korean Registry. Int J Hematol. 2013;97:749–757. - PubMed
-
- Hillmen P, Elebute M, Kelly R, Urbano-Ispizua A, Hill A, Rother RP, Khursigara G, Fu CL, Omine M, Browne P, et al. Long-term effect of the complement inhibitor eculizumab on kidney function in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Am J Hematol. 2010;85:553–559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

