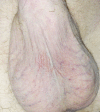
Sorafenib-induced Scrotal Eczema
- PMID: 26839524
- PMCID: PMC4735673
Sorafenib-induced Scrotal Eczema
Abstract
Sorafenib is an orally active, small-molecule multikinase inhibitor that blocks tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Studies have shown that it is a highly potent, selective inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors 2 and 3, platelet-derived growth factor-β, RAF, FLT-3, and c-Kit. This drug was recently approved for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma. We report a case of a patient treated with sorafenib for metastatic renal cell carcinoma who developed scrotal eczema.
Keywords: Hand-foot skin reaction; Scrotal eczema; Sorafenib.
Figures
References
-
- Haraldsdottir S, Li Q, Villalona-Calero MA, et al. Case of sorafenib-induced thyroid storm. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:e262–e264. - PubMed
-
- Yang CH, Lin WC, Chang CK, et al. Hand-foot skin reaction in patients treated with sorafenib: a clinicopathological study of cutaneous manifestations due to multitargeted kinase inhibitor therapy. Br J Dermatol. 2008;158:592–596. - PubMed
-
- Cuesta L, Betlloch I, Toledo F, et al. Severe sorafenibinduced hand-foot skin reaction. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:14. - PubMed
-
- Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, et al. Sorafenib blocks the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer Res. 2006;66:11851–11858. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous