Quantitative Analysis of Intestinal Flora of Uygur and Han Ethnic Chinese Patients with Ulcerative Colitis
- PMID: 26839545
- PMCID: PMC4709672
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/9186232
Quantitative Analysis of Intestinal Flora of Uygur and Han Ethnic Chinese Patients with Ulcerative Colitis
Abstract
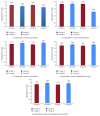
Aim. To study the correlation between intestinal flora and ulcerative colitis by analyzing the abundance of Bacteroides, Fusobacterium, Clostridium, Bifidobacterium spp., and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in the intestinal of ulcerative colitis (UC) patients and healthy controls with Uygur and Han ethnic. Methods. Bacterial genomic DNA was extracted from fecal samples and analyzed with real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to identify the abundance of Bacteroides, Fusobacterium, Clostridium, Bifidobacterium spp., and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii. Results. The samples from UC patients, Uygur and Han ethnic combined, had higher abundance of Bacteroides (P = 0.026) but lower Clostridium (P = 0.004), Bifidobacterium spp. (P = 0.009), and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii (P = 0.008) than those from healthy controls. Among UC patients, Bacteroides population was raised in acute UC patients (P ≤ 0.05), while the abundance of Clostridium, Bifidobacterium spp., Fusobacterium, and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii decreased (P ≤ 0.05) compared with the remission. In both UC patients group and control group, no difference was observed in the abundance of these 5 bacteria between the Han and the Uygur group. Conclusions. Variations in the abundance of these five bacterial strains in intestines may be associated with the occurrence of UC in Uygur and Han populations; however, these variations were not associated with ethnic difference.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Influence of Microbiota on Intestinal Immune System in Ulcerative Colitis and Its Intervention.Front Immunol. 2017 Nov 28;8:1674. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01674. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29234327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal flora differences between patients with ulcerative colitis of different ethnic groups in China.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Aug 13;100(32):e26932. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026932. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34397940 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of dominant gut microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Disease patients and healthy individuals: A case-control study.New Microbes New Infect. 2025 Feb 6;64:101567. doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2025.101567. eCollection 2025 Apr. New Microbes New Infect. 2025. PMID: 39991465 Free PMC article.
-
A decrease of the butyrate-producing species Roseburia hominis and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii defines dysbiosis in patients with ulcerative colitis.Gut. 2014 Aug;63(8):1275-83. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-304833. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Gut. 2014. PMID: 24021287
-
Enteric microbiota leads to new therapeutic strategies for ulcerative colitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Nov 14;20(42):15657-63. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15657. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25400449 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fusobacterium nucleatum Secretes Outer Membrane Vesicles and Promotes Intestinal Inflammation.mBio. 2021 Mar 2;12(2):e02706-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02706-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33653893 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary proline supplementation alters colonic luminal microbiota and bacterial metabolite composition between days 45 and 70 of pregnancy in Huanjiang mini-pigs.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2018 Jan 30;9:18. doi: 10.1186/s40104-018-0233-5. eCollection 2018. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29423216 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Microbiota on Intestinal Immune System in Ulcerative Colitis and Its Intervention.Front Immunol. 2017 Nov 28;8:1674. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01674. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29234327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Network pharmacology and in vivo experiment-based strategy to investigate mechanisms of JingFangFuZiLiZhong formula for ulcerative colitis.Ann Med. 2022 Dec;54(1):3219-3233. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2095665. Ann Med. 2022. PMID: 36382627 Free PMC article.
-
Indigo Naturalis Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice by Modulating the Intestinal Microbiota Community.Molecules. 2019 Nov 12;24(22):4086. doi: 10.3390/molecules24224086. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31726738 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

