Increased dosage of infliximab is a potential cause of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia
- PMID: 26839596
- PMCID: PMC4736477
- DOI: 10.1186/s13099-016-0086-4
Increased dosage of infliximab is a potential cause of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia
Abstract
Methods: Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia occasionally appears in immunodeficient patients. While several reports have shown that Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia occurred in the early phase of starting infliximab treatment in patients with Crohn's disease (CD), the present case suggests for the first time that an increased dosage of infliximab may also lead to pneumonia.
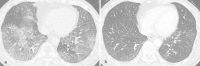
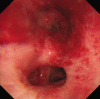
Results: A 51-year-old male had been taking 5 mg of infliximab for the treatment of CD for 10 years with no adverse events. Beginning in September 2013, the dose of infliximab had to be increased to 10 mg/kg because his status worsened. Thereafter, he complained of a fever and cough, and a CT scan revealed ground-glass opacities in the lower lobes of the bilateral lung with a crazy-paving pattern. Bronchoscopy detected swelling of the tracheal mucosa with obvious dilations of the vessels. A polymerase chain reaction using a bronchoalveolar lavage fluid sample detected specific sequences for Pneumocystis jirovecii; thus he was diagnosed with Pneumocystis carinii (jirovecii) pneumonia. After discontinuing infliximab and starting antibiotic treatment, his symptoms and CT findings were dramatically improved.
Conclusions: The administration of an increased dosage of infliximab can cause Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in CD patients.
Figures
References
-
- Mori S, Imamura F, Kiyofuji C, Ito K, Koga Y, Honda I, Sugimoto M. Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis as a complication of treatment with infliximab, anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha neutralizing antibody. Mod Rheumatol. 2006;16:58–62. doi: 10.3109/s10165-005-0454-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kasai S, Tokuda H, Otsuka Y, Ookohchi Y, Handa H, Emoto N, Yoshikawa M. Two cases of respiratory infection complicating treatment with infliximab. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2007;45:366–371. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

