Rating of Perceived Exertion and Physiological Responses in Water-Based Exercise
- PMID: 26839610
- PMCID: PMC4723186
- DOI: 10.1515/hukin-2015-0112
Rating of Perceived Exertion and Physiological Responses in Water-Based Exercise
Abstract
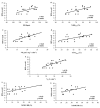
The aim of the present study was to relate the overall rating of perceived exertion (RPE-overall) with cardiorespiratory and neuromuscular variables during stationary running with the elbow flexion/extension performed with water-floating equipment. The sample consisted of eleven women that performed the water-based exercise at submaximal cadences. The heart rate, oxygen uptake, ventilation, and electromyographic signal (EMG) from biceps brachii (%EMG BB), triceps brachii (%EMG TB), biceps femoris (%EMG BF) and rectus femoris (%EMG RF) muscles were measured during the exercise, and the overall RPE was measured immediately following its completion. The Pearson product-moment linear correlation was used to investigate associations between the variables analyzed in the present study. Significant relationships were observed between the RPE-overall and all the cardiorespiratory variables, with the r values ranging from 0.60 to 0.70 (p<0.05). In addition, the RPE-overall showed a significant (p<0.05) relationship with %EMG BB (r=0.55) and %EMG BF (r=0.50). These results suggest an association between the RPE-overall with all cardiorespiratory and two neuromuscular variables during the execution of a water-based aerobic exercise using water-floating equipment.
Keywords: aquatic exercise; electromyographic signal; floating equipment; heart rate; minute ventilation; oxygen uptake.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correlation between rating of perceived exertion and physiological variables during the execution of stationary running in water at different cadences.J Strength Cond Res. 2011 Jan;25(1):155-62. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181bde2b5. J Strength Cond Res. 2011. PMID: 20093964
-
Cardiorespiratory and neuromuscular responses during water aerobics exercise performed with and without equipment.Int J Sports Med. 2011 Dec;32(12):916-23. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1283176. Epub 2011 Nov 3. Int J Sports Med. 2011. PMID: 22052026
-
Cardiorespiratory, neuromuscular and kinematic responses to stationary running performed in water and on dry land.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011 Jun;111(6):1157-66. doi: 10.1007/s00421-010-1747-5. Epub 2010 Dec 3. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21127897 Clinical Trial.
-
Kinesiological Analysis of Stationary Running Performed in Aquatic and Dry Land Environments.J Hum Kinet. 2015 Dec 30;49:5-14. doi: 10.1515/hukin-2015-0103. eCollection 2015 Dec 22. J Hum Kinet. 2015. PMID: 26839601 Free PMC article.
-
Perceived exertion : influence of age and cognitive development.Sports Med. 2006;36(11):911-28. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200636110-00001. Sports Med. 2006. PMID: 17052130 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between Oxygen Uptake, Heart Rate, and Perceived Effort in an Aquatic Incremental Test in Older Women.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Nov 11;17(22):8324. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17228324. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33187067 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrent and Construct Validation of a Scale for Rating Perceived Exertion in Aquatic Cycling for Young Men.J Sports Sci Med. 2019 Nov 19;18(4):695-707. eCollection 2019 Dec. J Sports Sci Med. 2019. PMID: 31827354 Free PMC article.
-
Discussion of "Concurrent and Construct Validation of a Scale for Rating Perceived Exertion in Aquatic Cycling for Young Men".J Sports Sci Med. 2020 Feb 24;19(1):231-234. eCollection 2020 Mar. J Sports Sci Med. 2020. PMID: 32132847 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Impact of a 10-Week Aqua Fitness Intervention on Physical Fitness and Psychosocial Measures in Inactive Healthy Adult Women.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Feb 6;13(3):334. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13030334. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39942523 Free PMC article.
-
Endurance in Long-Distance Swimming and the Use of Nutritional Aids.Nutrients. 2024 Nov 19;16(22):3949. doi: 10.3390/nu16223949. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39599736 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alberton CL, Antunes AH, Pinto SS, Tartaruga MP, Silva EM, Cadore EL, Kruel LFM. Correlation between rating of perceived exertion and physiological variables during the execution of stationary running in water at different cadences. J Strength Cond Res. 2011;25:155–162. - PubMed
-
- Alberton CL, Cadore EL, Pinto SS, Tartaruga MP, Silva EM, Kruel LFM. Cardiorespiratory, neuromuscular and kinematic responses to stationary running performed in water and on dry land. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011;111:1157–1166. - PubMed
-
- Alberton CL, Rothmann CRC, Pinto SS, Coertjens M, Kruel LFM. Oxygen consumption and rate of perceived exertion at different rhythms in water aerobics. Motriz. 2012;18:423–431.
-
- Bento PCB, Pereira G, Ugrinowitsch C, Rodacki ALF. The effects of a water-based exercise program on strength and functionality of older adults. J Aging Phys Act. 2012;20:469–483. - PubMed
-
- Borg G. Psychophysical scaling with applications in physical work and the perception of exertion. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1990;16:55–58. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
