Submucosal tunnel endoscopy: Peroral endoscopic myotomy and peroral endoscopic tumor resection
- PMID: 26839649
- PMCID: PMC4724034
- DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v8.i2.86
Submucosal tunnel endoscopy: Peroral endoscopic myotomy and peroral endoscopic tumor resection
Abstract
Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) is an innovative, minimally invasive, endoscopic treatment for esophageal achalasia and other esophageal motility disorders, emerged from the natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery procedures, and since the first human case performed by Inoue in 2008, showed exciting results in international level, with more than 4000 cases globally up to now. POEM showed superior characteristics than the standard 100-year-old surgical or laparoscopic Heller myotomy (LHM), not only for all types of esophageal achalasia [classical (I), vigorous (II), spastic (III), Chicago Classification], but also for advanced sigmoid type achalasia (S1 and S2), failed LHM, or other esophageal motility disorders (diffuse esophageal spasm, nutcracker esophagus or Jackhammer esophagus). POEM starts with a mucosal incision, followed by submucosal tunnel creation crossing the esophagogastric junction (EGJ) and myotomy. Finally the mucosal entry is closed with endoscopic clip placement. POEM permitted relatively free choice of myotomy length and localization. Although it is technically demanding procedure, POEM can be performed safely and achieves very good control of dysphagia and chest pain. Gastroesophageal reflux is the most common troublesome side effect, and is well controllable with proton pump inhibitors. Furthermore, POEM opened the era of submucosal tunnel endoscopy, with many other applications. Based on the same principles with POEM, in combination with new technological developments, such as endoscopic suturing, peroral endoscopic tumor resection (POET), is safely and effectively applied for challenging submucosal esophageal, EGJ and gastric cardia tumors (submucosal tumors), emerged from muscularis propria. POET showed up to know promising results, however, it is restricted to specialized centers. The present article reviews the recent data of POEM and POET and discussed controversial issues that need further study and future perspectives.
Keywords: Achalasia; EndoFLIP; Endoscopic submucosal dissection; Heller myotomy; LES; Laparoscopic myotomy; Minimally invasive surgery; Natural orifice transluminal endoscopy surgery; Per-oral endoscopic myotomy; Peroral endoscopic tumorectomy; Submucosal endoscopy; Transluminal technique.
Figures
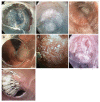
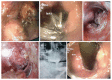
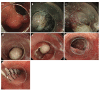
References
-
- Inoue H, Minami H, Kobayashi Y, Sato Y, Kaga M, Suzuki M, Satodate H, Odaka N, Itoh H, Kudo S. Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia. Endoscopy. 2010;42:265–271. - PubMed
-
- Kalloo AN, Singh VK, Jagannath SB, Niiyama H, Hill SL, Vaughn CA, Magee CA, Kantsevoy SV. Flexible transgastric peritoneoscopy: a novel approach to diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the peritoneal cavity. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;60:114–117. - PubMed
-
- Stavropoulos SN, Modayil RJ, Friedel D, Savides T. The International Per Oral Endoscopic Myotomy Survey (IPOEMS): a snapshot of the global POEM experience. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:3322–3338. - PubMed
-
- Zhou PH, Cai MY, Yao LQ, Zhong YS, Ren Z, Xu MD, Chen WF, Qin XY. [Peroral endoscopic myotomy for esophageal achalasia: report of 42 cases] Zhonghua Weichang Waike Zazhi. 2011;14:705–708. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

