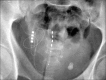
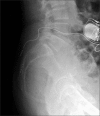
Caudal Neuromodulation with the Transforaminal Sacral Electrode (InterStim®): Experience in a Pain Center Regarding 12 Implants
- PMID: 26839667
- PMCID: PMC4731547
- DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.1.23
Caudal Neuromodulation with the Transforaminal Sacral Electrode (InterStim®): Experience in a Pain Center Regarding 12 Implants
Abstract
Background: Sacral nerve stimulation is a therapeutic option with demonstrated efficacy for conditions presenting with perineal pain caused by different etiologies. We aimed to assess whether a sacral electrode (InterStim®, Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN, USA) inserted through the caudal pathway is able to offer an acceptable level of sacral stimulation and rate of catheter migration.
Methods: We present 12 patients with pelvic pain who received sacral neuromodulation via the sacral hiatus with the InterStim electrode. We evaluated patient satisfaction as well as migration and removal of the electrode, if necessary.
Results: Our experience included 12 patients, 10 women and two men, with a mean age of 60 years. In eight of the 12 patients, the initial therapy was effective, and the final system implantation was performed. During subsequent follow-up, patient satisfaction was good. To date, there have been no cases of electrode displacement or migration.
Conclusions: The caudal insertion of the InterStim electrode, with its own fixation system, and initially designed for transsacral insertion, appears in our experience to be a satisfactory option which can minimize electrode displacements, achieving similar results in therapeutic efficacy and causing no difficulties in removal.
Keywords: Implantable neurostimulator; Outcome assessment; Pain; Perineum; Sacrococcygeal region; Sacrum; Spinal cord stimulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of sacral neuromodulation system with new six-contact points electrode in pigs.Neurourol Urodyn. 2019 Apr;38(4):1038-1043. doi: 10.1002/nau.23956. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Neurourol Urodyn. 2019. PMID: 30843257
-
A rare case of tined lead migration of InterStim device into the rectum with subsequent novel combined surgical-endoscopic removal technique.Turk J Urol. 2020 Nov;46(6):492-495. doi: 10.5152/tud.2020.20320. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Turk J Urol. 2020. PMID: 33016870 Free PMC article.
-
Radiographic Position of the Electrode as a Predictor of the Outcome of InterStim Therapy.Int Neurourol J. 2017 Dec;21(4):289-294. doi: 10.5213/inj.1734942.471. Epub 2017 Dec 31. Int Neurourol J. 2017. PMID: 29298468 Free PMC article.
-
Sacral nerve neuromodulation (InterStim). Part I: Review of the InterStim system.Urol Nurs. 2008 Feb;28(1):15-20. Urol Nurs. 2008. PMID: 18335692 Review.
-
Sacral Neuromodulation for Genitourinary Problems.Prog Neurol Surg. 2015;29:192-9. doi: 10.1159/000434671. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Prog Neurol Surg. 2015. PMID: 26394134 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of transforaminal epidural polydeoxyribonucleotide injections on lumbosacral radiculopathy: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jun;96(25):e7174. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007174. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28640096 Free PMC article.
-
Neuromodulation for Chronic Pelvic Pain.Curr Urol Rep. 2018 Mar 26;19(5):32. doi: 10.1007/s11934-018-0783-2. Curr Urol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29582185 Review.
-
Neuromodulation for Management of Chronic Pelvic Pain: A Comprehensive Review.Pain Ther. 2022 Dec;11(4):1137-1177. doi: 10.1007/s40122-022-00430-9. Epub 2022 Sep 15. Pain Ther. 2022. PMID: 36109459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sacral neuromodulation treating chronic pelvic pain: a meta-analysis and systematic review of the literature.Int Urogynecol J. 2019 Jul;30(7):1023-1035. doi: 10.1007/s00192-019-03898-w. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Int Urogynecol J. 2019. PMID: 30874835
References
-
- Aló KM, McKay E. Selective Nerve Root Stimulation (SNRS) for the treatment of intractable pelvic pain and motor dysfunction: a case report. Neuromodulation. 2001;4:19–23. - PubMed
-
- Alo KM, Yland MJ, Redko V, Feler C, Naumann C. Lumbar and sacral nerve root stimulation (NRS) in the treatment of chronic pain: a novel anatomic approach and neuro stimulation technique. Neuromodulation. 1999;2:23–31. - PubMed
-
- Feler CA, Whitworth LA, Fernandez J. Sacral neuromodulation for chronic pain conditions. Anesthesiol Clin North America. 2003;21:785–795. - PubMed
-
- Kohli N, Rosenblatt PL. Neuromodulation techniques for the treatment of the overactive bladder. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2002;45:218–232. - PubMed
-
- Chodez M, Trilling B, Thuillier C, Boillot B, Barbois S, Faucheron JL. Results of sacral nerve neuromodulation for double incontinence in adults. Tech Coloproctol. 2014;18:1147–1151. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources