Expression and Function of the Endocannabinoid System in the Retina and the Visual Brain
- PMID: 26839718
- PMCID: PMC4709729
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/9247057
Expression and Function of the Endocannabinoid System in the Retina and the Visual Brain
Abstract
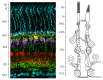
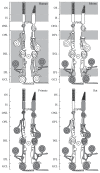
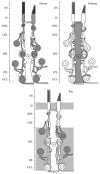
Endocannabinoids are important retrograde modulators of synaptic transmission throughout the nervous system. Cannabinoid receptors are seven transmembrane G-protein coupled receptors favoring Gi/o protein. They are known to play an important role in various processes, including metabolic regulation, craving, pain, anxiety, and immune function. In the last decade, there has been a growing interest for endocannabinoids in the retina and their role in visual processing. The purpose of this review is to characterize the expression and physiological functions of the endocannabinoid system in the visual system, from the retina to the primary visual cortex, with a main interest regarding the retina, which is the best-described area in this system so far. It will show that the endocannabinoid system is widely present in the retina, mostly in the through pathway where it can modulate neurotransmitter release and ion channel activity, although some evidence also indicates possible mechanisms via amacrine, horizontal, and Müller cells. The presence of multiple endocannabinoid ligands, synthesizing and catabolizing enzymes, and receptors highlights various pharmacological targets for novel therapeutic application to retinal diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Vertical and Horizontal Pathways in the Monkey Retina Are Modulated by Typical and Atypical Cannabinoid Receptors.Cells. 2021 Nov 13;10(11):3160. doi: 10.3390/cells10113160. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of endocannabinoids in pain modulation.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Feb;27(1):64-80. doi: 10.1111/fcp.12008. Epub 2013 Jan 2. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23278562 Review.
-
The Endocannabinoid System in the Retina: From Physiology to Practical and Therapeutic Applications.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:2916732. doi: 10.1155/2016/2916732. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 26881099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From endocannabinoid profiling to 'endocannabinoid therapeutics'.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2009 Jun;13(3):321-31. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.04.615. Epub 2009 Jun 3. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2009. PMID: 19497779 Review.
-
The endocannabinoid system: current pharmacological research and therapeutic possibilities.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2006 Feb;98(2):124-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2006.pto_376.x. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2006. PMID: 16445584 Review.
Cited by
-
Circadian clock organization in the retina: From clock components to rod and cone pathways and visual function.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2023 May;94:101119. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2022.101119. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2023. PMID: 36503722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Vertical and Horizontal Pathways in the Monkey Retina Are Modulated by Typical and Atypical Cannabinoid Receptors.Cells. 2021 Nov 13;10(11):3160. doi: 10.3390/cells10113160. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations of endocannabinoid signaling and microglia reactivity in the retinas of AD-like mice precede the onset of hippocampal β-amyloid plaques.J Neurochem. 2025 Feb;169(2):e16256. doi: 10.1111/jnc.16256. Epub 2024 Nov 18. J Neurochem. 2025. PMID: 39556462 Free PMC article.
-
Potential for endocannabinoid system modulation in ocular pain and inflammation: filling the gaps in current pharmacological options.Neuronal Signal. 2018 Nov 2;2(4):NS20170144. doi: 10.1042/NS20170144. eCollection 2018 Dec. Neuronal Signal. 2018. PMID: 32714590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabinoid signaling promotes the de-differentiation and proliferation of Müller glia-derived progenitor cells.Glia. 2021 Oct;69(10):2503-2521. doi: 10.1002/glia.24056. Epub 2021 Jul 7. Glia. 2021. PMID: 34231253 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

