Protective effects of the extracts of Barringtonia racemosa shoots against oxidative damage in HepG2 cells
- PMID: 26839752
- PMCID: PMC4734433
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.1628
Protective effects of the extracts of Barringtonia racemosa shoots against oxidative damage in HepG2 cells
Abstract
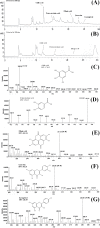
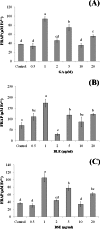
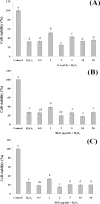
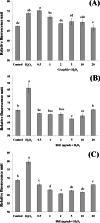
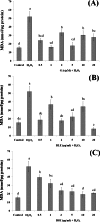
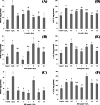
Barringtonia racemosa is a tropical plant with medicinal values. In this study, the ability of the water extracts of the leaf (BLE) and stem (BSE) from the shoots to protect HepG2 cells against oxidative damage was studied. Five major polyphenolic compounds consisting of gallic acid, ellagic acid, protocatechuic acid, quercetin and kaempferol were identified using HPLC-DAD and ESI-MS. Cell viability assay revealed that BLE and BSE were non-cytotoxic (cell viabilities >80%) at concentration less than 250 µg/ml and 500 µg/ml, respectively. BLE and BSE improved cellular antioxidant status measured by FRAP assay and protected HepG2 cells against H2O2-induced cytotoxicity. The extracts also inhibited lipid peroxidation in HepG2 cells as well as the production of reactive oxygen species. BLE and BSE could also suppress the activities of superoxide dismutase and catalase during oxidative stress. The shoots of B. racemosa can be an alternative bioactive ingredient in the prevention of oxidative damage.
Keywords: Antioxidant enzymes; Barringtonia racemosa; HPLC-ESI-MS; Lipid peroxidation; Oxidative stress; Polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Boulton DW, Walle UK, Walle T. Extensive binding of the bioflavonoid quercetin to human plasma proteins. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 1998;50:243–249. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

