MutAid: Sanger and NGS Based Integrated Pipeline for Mutation Identification, Validation and Annotation in Human Molecular Genetics
- PMID: 26840129
- PMCID: PMC4739551
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147697
MutAid: Sanger and NGS Based Integrated Pipeline for Mutation Identification, Validation and Annotation in Human Molecular Genetics
Abstract
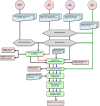
Traditional Sanger sequencing as well as Next-Generation Sequencing have been used for the identification of disease causing mutations in human molecular research. The majority of currently available tools are developed for research and explorative purposes and often do not provide a complete, efficient, one-stop solution. As the focus of currently developed tools is mainly on NGS data analysis, no integrative solution for the analysis of Sanger data is provided and consequently a one-stop solution to analyze reads from both sequencing platforms is not available. We have therefore developed a new pipeline called MutAid to analyze and interpret raw sequencing data produced by Sanger or several NGS sequencing platforms. It performs format conversion, base calling, quality trimming, filtering, read mapping, variant calling, variant annotation and analysis of Sanger and NGS data under a single platform. It is capable of analyzing reads from multiple patients in a single run to create a list of potential disease causing base substitutions as well as insertions and deletions. MutAid has been developed for expert and non-expert users and supports four sequencing platforms including Sanger, Illumina, 454 and Ion Torrent. Furthermore, for NGS data analysis, five read mappers including BWA, TMAP, Bowtie, Bowtie2 and GSNAP and four variant callers including GATK-HaplotypeCaller, SAMTOOLS, Freebayes and VarScan2 pipelines are supported. MutAid is freely available at https://sourceforge.net/projects/mutaid.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

