Applications and Challenges for Use of Cell-Penetrating Peptides as Delivery Vectors for Peptide and Protein Cargos
- PMID: 26840305
- PMCID: PMC4783919
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17020185
Applications and Challenges for Use of Cell-Penetrating Peptides as Delivery Vectors for Peptide and Protein Cargos
Abstract
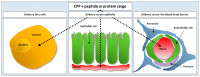
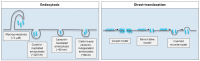
The hydrophilic nature of peptides and proteins renders them impermeable to cell membranes. Thus, in order to successfully deliver peptide and protein-based therapeutics across the plasma membrane or epithelial and endothelial barriers, a permeation enhancing strategy must be employed. Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) constitute a promising tool and have shown applications for peptide and protein delivery into cells as well as across various epithelia and the blood-brain barrier (BBB). CPP-mediated delivery of peptides and proteins may be pursued via covalent conjugation of the CPP to the cargo peptide or protein or via physical complexation obtained by simple bulk-mixing of the CPP with its cargo. Both approaches have their pros and cons, and which is the better choice likely relates to the physicochemical properties of the CPP and its cargo as well as the route of administration, the specific barrier and the target cell. Besides the physical barrier, a metabolic barrier must be taken into consideration when applying peptide-based delivery vectors, such as the CPPs, and stability-enhancing strategies are commonly employed to prolong the CPP half-life. The mechanisms by which CPPs translocate cell membranes are believed to involve both endocytosis and direct translocation, but are still widely investigated and discussed. The fact that multiple factors influence the mechanisms responsible for cellular CPP internalization and the lack of sensitive methods for detection of the CPP, and in some cases the cargo, further complicates the design and conduction of conclusive mechanistic studies.
Keywords: biological barriers; cell-penetrating peptides; delivery vectors; drug delivery; peptide and protein drugs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cell-Penetrating Peptides as Carriers for Oral Delivery of Biopharmaceuticals.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016 Feb;118(2):99-106. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.12515. Epub 2015 Dec 10. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26525297 Review.
-
The Current Role of Cell-Penetrating Peptides in Cancer Therapy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1030:279-295. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-66095-0_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29081059 Review.
-
Covalent conjugation and non-covalent complexation strategies for intracellular delivery of proteins using cell-penetrating peptides.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Jul;176:116910. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116910. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38852512 Review.
-
Cell-penetrating peptides as tools to enhance non-injectable delivery of biopharmaceuticals.Tissue Barriers. 2016 Apr 18;4(2):e1178369. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2016.1178369. eCollection 2016 Apr-Jun. Tissue Barriers. 2016. PMID: 27358757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic, cellular, and structural characterization of the membrane potential-dependent cell-penetrating peptide translocation pore.Elife. 2021 Oct 29;10:e69832. doi: 10.7554/eLife.69832. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34713805 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Structural Elucidation of the Cell-Penetrating Penetratin Peptide in Model Membranes at the Atomic Level: Probing Hydrophobic Interactions in the Blood-Brain Barrier.Biochemistry. 2016 Sep 6;55(35):4982-96. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00518. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27532224 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Cell Penetrating Peptides as a Promising Drug Carrier to Combat Viral Infections.Mol Biotechnol. 2023 Sep;65(9):1387-1402. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00679-1. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Mol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36719639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-Penetrating Antimicrobial Peptides with Anti-Infective Activity against Intracellular Pathogens.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Dec 8;11(12):1772. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11121772. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Initial Evaluation of Antibody-conjugates Modified with Viral-derived Peptides for Increasing Cellular Accumulation and Improving Tumor Targeting.J Vis Exp. 2018 Mar 8;(133):55440. doi: 10.3791/55440. J Vis Exp. 2018. PMID: 29578523 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Dendrons as Agents for Intracellular Delivery.J Am Chem Soc. 2021 Sep 1;143(34):13513-13518. doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c07240. Epub 2021 Aug 19. J Am Chem Soc. 2021. PMID: 34410116 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Derossi D., Joliot A.H., Chassaing G., Prochiantz A. The third helix of the Antennapedia homeodomain translocates through biological membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:10444–10450. - PubMed
-
- Ezzat K., El Andaloussi S., Zaghloul E.M., Lehto T., Lindberg S., Moreno P.M.D., Viola J.R., Magdy T., Abdo R., Guterstam P., et al. PepFect 14, a novel cell-penetrating peptide for oligonucleotide delivery in solution and as solid formulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:5284–5298. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr072. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

