Different Effects of Three Selected Lactobacillus Strains in Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in BALB/c Mice
- PMID: 26840426
- PMCID: PMC4739695
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148241
Different Effects of Three Selected Lactobacillus Strains in Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in BALB/c Mice
Abstract
Aim: To analyze the changes of different Lactobacillus species in ulcerative colitis patients and to further assess the therapeutic effects of selected Lactobacillus strains on dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced experimental colitis in BALB/c mice.
Methods: Forty-five active ulcerative colitis (UC) patients and 45 population-based healthy controls were enrolled. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification and real-time PCR were performed for qualitative and quantitative analyses, respectively, of the Lactobacillus species in UC patients. Three Lactobacillus strains from three species were selected to assess the therapeutic effects on experimental colitis. Sixty 8-week-old BALB/c mice were divided into six groups. The five groups that had received DSS were administered normal saline, mesalazine, L. fermentum CCTCC M206110 strain, L. crispatus CCTCC M206119 strain, or L. plantarum NCIMB8826 strain. We assessed the severity of colitis based on disease activity index (DAI), body weight loss, colon length, and histologic damage.
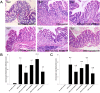
Results: The detection rate of four of the 11 Lactobacillus species decreased significantly (P < 0.05), and the detection rate of two of the 11 Lactobacillus species increased significantly (P < 0.05) in UC patients. Relative quantitative analysis revealed that eight Lactobacillus species declined significantly in UC patients (P < 0.05), while three Lactobacillus species increased significantly (P < 0.05). The CCTCC M206110 treatment group had less weight loss and colon length shortening, lower DAI scores, and lower histologic scores (P < 0.05), while the CCTCC M206119 treatment group had greater weight loss and colon length shortening, higher histologic scores, and more severe inflammatory infiltration (P < 0.05). NCIMB8826 improved weight loss and colon length shortening (P < 0.05) with no significant influence on DAI and histologic damage in the colitis model.
Conclusions: Administration of an L. crispatus CCTCC M206119 supplement aggravated DSS-induced colitis. L. fermentum CCTCC M206110 proved to be effective at attenuating DSS-induced colitis. The potential probiotic effect of L. plantarum NCIMB8826 on UC has yet to be assessed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lactobacillus crispatus M206119 exacerbates murine DSS-colitis by interfering with inflammatory responses.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 May 21;18(19):2344-56. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i19.2344. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22654425 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of selected Lactobacillus strains on dextran sulfate sodium-induced mouse colitis model.Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2020 Jun 12;67(2):138-142. doi: 10.1556/030.2020.00834. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2020. PMID: 32554841
-
Oral administration of Lactobacillus paracasei alleviates clinical symptoms of colitis induced by dextran sulphate sodium salt in BALB/c mice.Benef Microbes. 2014 Sep;5(3):315-22. doi: 10.3920/BM2013.0041. Benef Microbes. 2014. PMID: 24889889
-
Progress on the mechanisms of Lactobacillus plantarum to improve intestinal barrier function in ulcerative colitis.J Nutr Biochem. 2024 Feb;124:109505. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2023.109505. Epub 2023 Oct 26. J Nutr Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37890709 Review.
-
Evaluating the Therapeutic Efficacy of Lactobacillus Strains in the Management of Ulcerative Colitis: An Overview of Recent Advances.Curr Pharm Des. 2025;31(6):413-421. doi: 10.2174/0113816128322653240925115114. Curr Pharm Des. 2025. PMID: 39385420 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of Probiotic VSL#3 Inhibiting NF-κB and TNF-α on Colitis through TLR4-NF-κB Signal Pathway.Iran J Public Health. 2019 Jul;48(7):1292-1300. Iran J Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31497551 Free PMC article.
-
Pomegranate peel extract alters the microbiome in mice and dysbiosis caused by Citrobacter rodentium infection.Food Sci Nutr. 2019 Jul 7;7(8):2565-2576. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1106. eCollection 2019 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31428344 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal release of biofilm-like microcolonies encased in calcium-pectinate beads increases probiotic properties of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2020 Oct 28;6(1):44. doi: 10.1038/s41522-020-00159-3. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2020. PMID: 33116127 Free PMC article.
-
Salt-responsive gut commensal modulates TH17 axis and disease.Nature. 2017 Nov 30;551(7682):585-589. doi: 10.1038/nature24628. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Nature. 2017. PMID: 29143823 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Dietary Grape Seed Meal Bioactive Compounds on the Colonic Microbiota of Weaned Piglets With Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Colitis Used as an Inflammatory Model.Front Vet Sci. 2020 Feb 26;7:31. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00031. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 32161762 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanauer SB. Inflammatory bowel disease: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and therapeutic opportunities. Inflammatory bowel diseases. 2006;12 Suppl 1:S3–9. . - PubMed
-
- Sartor RB. Therapeutic manipulation of the enteric microflora in inflammatory bowel diseases: antibiotics, probiotics, and prebiotics. Gastroenterology. 2004;126(6):1620–33. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

