Can Spectral CT Imaging Improve the Differentiation between Malignant and Benign Solitary Pulmonary Nodules?
- PMID: 26840459
- PMCID: PMC4739615
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147537
Can Spectral CT Imaging Improve the Differentiation between Malignant and Benign Solitary Pulmonary Nodules?
Abstract
Purpose: To quantitatively assess the value of dual-energy CT (DECT) in differentiating malignancy and benignity of solitary pulmonary nodules.
Materials and methods: Sixty-three patients with solitary pulmonary nodules detected by CT plain scan underwent contrast enhanced CT scans in arterial phase (AP) and venous phase (VP) with spectral imaging mode for tumor type differentiation. The Gemstone Spectral Imaging (GSI) viewer was used for image display and data analysis. Region of interest was placed on the relatively homogeneous area of the nodule to measure iodine concentration (IC) on iodine-based material decomposition images and CT numbers on monochromatic image sets to generate spectral HU curve. Normalized IC (NIC), slope of the spectral HU curve (λHU) and net CT number enhancement on 70keV images were calculated. The two-sample t-test was used to compare quantitative parameters. Receiver operating characteristic curves were generated to calculate sensitivity and specificity.
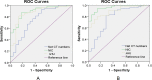
Results: There were 63 nodules, with 37 malignant nodules (59%) and 26 benign nodules (41%). NIC, λHU and net CT number enhancement on 70keV images for malignant nodules were all greater than those of benign nodules. NIC and λHU had intermediate to high performances to differentiate malignant nodules from benign ones with the areas under curve of 0.89 and 0.86 respectively in AP, 0.96 and 0.89 respectively in VP. Using 0.30 as a threshold value for NIC in VP, one could obtain sensitivity of 93.8% and specificity of 85.7% for differentiating malignant from benign solitary pulmonary nodules. These values were statistically higher than the corresponding values of 74.2% and 53.8% obtained with the conventional CT number enhancement.
Conclusions: DECT imaging with GSI mode provides more promising value in quantitative way for distinguishing malignant nodules from benign ones than CT enhancement numbers.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
A pilot study using low-dose Spectral CT and ASIR (Adaptive Statistical Iterative Reconstruction) algorithm to diagnose solitary pulmonary nodules.BMC Med Imaging. 2015 Nov 17;15:54. doi: 10.1186/s12880-015-0096-6. BMC Med Imaging. 2015. PMID: 26576676 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Gemstone Spectral Computed Tomography Imaging in the Characterization of Solitary Pulmonary Nodules: Preliminary Result.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2016 Nov/Dec;40(6):907-911. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000000469. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2016. PMID: 27529680
-
Spectral CT Analysis of Solitary Pulmonary Nodules for Differentiating Malignancy from Benignancy: The Value of Iodine Concentration Spatial Distribution Difference.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Dec 9;2018:4830659. doi: 10.1155/2018/4830659. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30627561 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dual-energy computed tomography characterization of solitary pulmonary nodules.J Thorac Imaging. 2010 Nov;25(4):301-10. doi: 10.1097/RTI.0b013e3181e16232. J Thorac Imaging. 2010. PMID: 21042068 Review.
-
Multidetector CT of solitary pulmonary nodules.Radiol Clin North Am. 2010 Jan;48(1):141-55. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2009.09.005. Radiol Clin North Am. 2010. PMID: 19995633 Review.
Cited by
-
Preoperative diagnosis of solitary pulmonary nodules with a novel hematological index model based on circulating tumor cells.Front Oncol. 2023 May 3;13:1150539. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1150539. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37207165 Free PMC article.
-
Value of dual-layer spectral detector computed tomography in the diagnosis of benign/malignant solid solitary pulmonary nodules and establishment of a prediction model.Front Oncol. 2023 May 5;13:1147479. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1147479. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37213284 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative parameters of enhanced dual-energy computed tomography for differentiating lung cancers from benign lesions in solid pulmonary nodules.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 6;12:1027985. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1027985. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36276069 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-energy computed tomography iodine uptake in differential diagnosis of inflammatory and malignant pulmonary nodules.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2022 Nov;28(6):563-568. doi: 10.5152/dir.2022.201091. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2022. PMID: 36550756 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of gastric cancer and its histological type based on iodine concentration in spectral CT.Cancer Imaging. 2018 Nov 9;18(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s40644-018-0176-2. Cancer Imaging. 2018. PMID: 30413174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Winer-Muram HT. The solitary pulmonary nodule. Radiology. 2006;239(1):34–49. - PubMed
-
- Swensen SJ, Yamashita K, McCollough CH, Viggiano RW, Midthun DE, Patz EF Jr, et al. Lung nodules: dual-kilovolt peak analysis with CT—multicenter study. Radiology. 2000;214(1):81–85. - PubMed
-
- Swensen SJ, Viggiano RW, Midthun DE, Müller NL, Sherrick A, Yamashita K, et al. Lung nodule enhancement at CT: multicenter study. Radiology. 2000;214(1): 73–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

