Bevacizumab specifically decreases elevated levels of circulating KIT+CD11b+ cells and IL-10 in metastatic breast cancer patients
- PMID: 26840567
- PMCID: PMC4905463
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7097
Bevacizumab specifically decreases elevated levels of circulating KIT+CD11b+ cells and IL-10 in metastatic breast cancer patients
Abstract
Background: Whether bevacizumab exerts its anti-tumor properties through systemic effects beyond local inhibition of angiogenesis and how these effects can be monitored in patients, remain largely elusive. To address these questions, we investigated bone marrow-derived cells and cytokines in the peripheral blood of metastatic breast cancer patients undergoing therapy with bevacizumab.
Methods: Circulating endothelial cells (CEC), circulating endothelial progenitor (CEP) and circulating CD11b+ cells in metastatic breast cancer patients before and during therapy with paclitaxel alone (n = 11) or in combination with bevacizumab (n = 10) were characterized using flow cytometry, real time PCR and RNASeq. Circulating factors were measured by ELISA. Aged-matched healthy donors were used as baseline controls (n = 12).
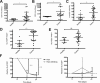
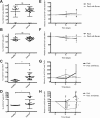
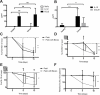
Results: Breast cancer patients had elevated frequencies of CEC, CEP, TIE2+CD11b+ and KIT+CD11b+ cell subsets. CEC decreased during therapy, irrespective of bevacizumab, while TIE2+CD11b+ remained unchanged. KIT+CD11b+ cells decreased in response to paclitaxel with bevacizumab, but not paclitaxel alone. Cancer patients expressed higher mRNA levels of the M2 polarization markers CD163, ARG1 and IL-10 in CD11b+ cells and increased levels of the M2 cytokines IL-10 and CCL20 in plasma. M1 activation markers and cytokines were low or equally expressed in cancer patients compared to healthy donors. Chemotherapy with paclitaxel and bevacizumab, but not with paclitaxel alone, significantly decreased IL-10 mRNA in CD11b+ cells and IL-10 protein in plasma.
Conclusions: This pilot study provides evidence of systemic immunomodulatory effects of bevacizumab and identified circulating KIT+CD11b+ cells and IL-10 as candidate biomarkers of bevacizumab activity in metastatic breast cancer patients.
Keywords: IL-10; KIT; angiogenesis; breast cancer; monocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Laurent J, Touvrey C, Botta F, Kuonen F, Ruegg C. Emerging paradigms and questions on pro-angiogenic bone marrow-derived myelomonocytic cells. Int J Dev Biol. 2011;55:527–534. - PubMed
-
- Katz OB, Shaked Y. Host effects contributing to cancer therapy resistance. Drug Resist Updat. 2015;19:33–42. - PubMed
-
- Mancuso P, Bertolini F. Circulating endothelial cells as biomarkers in clinical oncology. Microvasc Res. 2010;79:224–228. - PubMed
-
- Shaked Y, Henke E, Roodhart JM, Mancuso P, Langenberg MH, Colleoni M, Daenen LG, Man S, Xu P, Emmenegger U, Tang T, Zhu Z, Witte L, et al. Rapid chemotherapy-induced acute endothelial progenitor cell mobilization: implications for antiangiogenic drugs as chemosensitizing agents. Cancer Cell. 2008;14:263–273. - PMC - PubMed
-
- DeNardo DG, Brennan DJ, Rexhepaj E, Ruffell B, Shiao SL, Madden SF, Gallagher WM, Wadhwani N, Keil SD, Junaid SA, Rugo HS, Hwang ES, Jirstrom K, et al. Leukocyte complexity predicts breast cancer survival and functionally regulates response to chemotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2011;1:54–67. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

