Therapeutic Efficacy of an ω-3-Fatty Acid-Containing 17-β Estradiol Nano-Delivery System against Experimental Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 26840601
- PMCID: PMC4740455
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147337
Therapeutic Efficacy of an ω-3-Fatty Acid-Containing 17-β Estradiol Nano-Delivery System against Experimental Atherosclerosis
Abstract
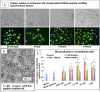
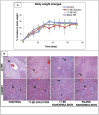
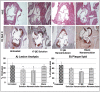
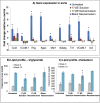
Atherosclerosis and its consequences remain prevalent clinical challenges throughout the world. Initiation and progression of atherosclerosis involves a complex, dynamic interplay among inflammation, hyperlipidemia, and endothelial dysfunction. A multicomponent treatment approach targeted for delivery within diseased vessels could prove beneficial in treating atherosclerosis. This study was undertaken to evaluate the multimodal effects of a novel ω-3-fatty acid-rich, 17-β-estradiol (17-βE)-loaded, CREKA-peptide-modified nanoemulsion system on experimental atherosclerosis. In vitro treatment of cultured human aortic endothelial cells (ECs) with the 17-βE-loaded, CREKA-peptide-modified nanoemulsion system increased cellular nitrate/nitrite, indicating improved nitric oxide formation. In vivo, systemic administration of this nanoemulsion system to apolipoprotein-E knock out (ApoE-/-) mice fed a high-fat diet significantly improved multiple parameters related to the etiology and development of occlusive atherosclerotic vasculopathy: lesion area, circulating plasma lipid levels, and expression of aortic-wall inflammatory markers. These salutary effects were attributed selectively to the 17-βE and/or ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid components of the nano-delivery system. At therapeutic doses, the 17-βE-loaded, CREKA-peptide modified nanoemulsion system appeared to be biocompatible in that it elicited no apparent adverse/toxic effects, as indexed by body weight, plasma alanine aminotransferase/aspartate aminotransferase levels, and liver and kidney histopathology. The study demonstrates the therapeutic potential of a novel, 17-βE-loaded, CREKA-peptide-modified nanoemulsion system against atherosclerosis in a multimodal fashion by reducing lesion size, lowering the levels of circulating plasma lipids and decreasing the gene expression of inflammatory markers associated with the disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Meyer MR, Haas E, Barton M. Gender differences of cardiovascular disease: new perspectives for estrogen receptor signaling. Hypertension. 2006;47: 1019–1026. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

