Achieving sustained virologic response after interferon-free hepatitis C virus treatment correlates with hepatic interferon gene expression changes independent of cirrhosis
- PMID: 26840694
- PMCID: PMC5021171
- DOI: 10.1111/jvh.12510
Achieving sustained virologic response after interferon-free hepatitis C virus treatment correlates with hepatic interferon gene expression changes independent of cirrhosis
Abstract
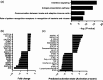
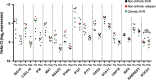
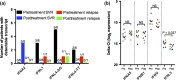
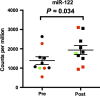
Chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection can now be treated with oral directly acting antiviral agents, either with or without ribavirin (RBV). Virologic relapse after treatment can occur, and in some studies was more common in cirrhotic subjects. We previously observed changes in hepatic immunity during interferon (IFN)-free therapy that correlated with favourable outcome in subjects with early liver disease. Here, we compared changes in endogenous IFN pathways during IFN-free, RBV-free therapy between cirrhotic and noncirrhotic subjects. mRNA and microRNA (miRNA) expression analyses were performed on paired pre- and post-treatment liver biopsies from genotype-1 HCV subjects treated with sofosbuvir/ledipasvir (SOF/LDV) for 12 weeks (n = 4, 3 cirrhotics) or SOF/LDV combined with GS-9669 or GS-9451 for 6 weeks (n = 6, 0 cirrhotics). Nine of ten subjects achieved a sustained virologic response (SVR), while one noncirrhotic subject relapsed. Hepatic IFN-stimulated gene expression decreased with treatment in the liver of all subjects, with no observable impact of cirrhosis. Hepatic gene expression of type III IFNs (IFNL1, IFNL3, IFNL4-ΔG) similarly decreased with treatment, while IFNA2 expression, undetectable in all subjects pretreatment, was detected post-treatment in three subjects who achieved a SVR. Only the subject who relapsed had detectable IFNL4-ΔG expression in post-treatment liver. Other IFNs had no change in gene expression (IFNG, IFNB1, IFNA5) or could not be detected. Although expression of multiple hepatic miRNAs changed with treatment, many miRNAs previously implicated in HCV replication and IFN signalling had unchanged expression. In conclusion, favourable treatment outcome during IFN-free HCV therapy is associated with changes in the host IFN response regardless of cirrhosis.
Keywords: cirrhosis; endogenous interferons; hepatitis C virus; interferon-free therapy; treatment relapse.
© 2016 The Authors. Journal of Viral Hepatitis published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endogenous intrahepatic IFNs and association with IFN-free HCV treatment outcome.J Clin Invest. 2014 Aug;124(8):3352-63. doi: 10.1172/JCI75938. Epub 2014 Jul 1. J Clin Invest. 2014. PMID: 24983321 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of hepatitis C virus recurrence after transplantation with sofosbuvir/ledipasvir: The role of ribavirin.Transpl Infect Dis. 2017 Feb;19(1). doi: 10.1111/tid.12647. Epub 2017 Jan 11. Transpl Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 27943544
-
Dynamic Changes of Post-Translationally Modified Forms of CXCL10 and Soluble DPP4 in HCV Subjects Receiving Interferon-Free Therapy.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 16;10(7):e0133236. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133236. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26181438 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase III results of Boceprevir in treatment naïve patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1.Liver Int. 2012 Feb;32 Suppl 1:27-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2011.02725.x. Liver Int. 2012. PMID: 22212568 Review.
-
Genetic Polymorphisms within Interferon-λ Region and Interferon-λ3 in the Human Pathophysiology: Their Contribution to Outcome, Treatment, and Prevention of Infections with Hepatotropic Viruses.Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(25):4832-4851. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180719121142. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30027841 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of patients treated with direct-acting anti-viral therapy for chronic hepatitis C and their risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in Hong Kong.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Jan 25;24(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-03099-2. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38273255 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid changes in peripheral lymphocyte concentrations during interferon-free treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection.Hepatol Commun. 2017 Sep;1(7):586-594. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1074. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Hepatol Commun. 2017. PMID: 29202115 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology and Elimination of HCV-Related Liver Disease.Viruses. 2018 Oct 6;10(10):545. doi: 10.3390/v10100545. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30301201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrahepatic Viral Kinetics During Direct-Acting Antivirals for Hepatitis C in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Coinfection: The AIDS Clinical Trials Group A5335S Substudy.J Infect Dis. 2020 Jul 23;222(4):601-610. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa126. J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32201883 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Recovery of natural killer cells is mainly in post-treatment period in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with sofosbuvir plus ledipasvir.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Oct 28;24(40):4554-4564. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i40.4554. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30386105 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

