Ca2+ Effects on ATP Production and Consumption Have Regulatory Roles on Oscillatory Islet Activity
- PMID: 26840737
- PMCID: PMC4744176
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.11.3526
Ca2+ Effects on ATP Production and Consumption Have Regulatory Roles on Oscillatory Islet Activity
Abstract
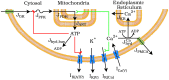
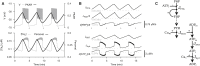
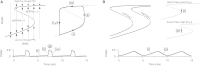
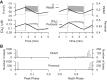
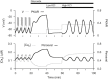
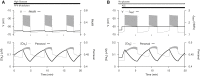
Pancreatic islets respond to elevated blood glucose by secreting pulses of insulin that parallel oscillations in β-cell metabolism, intracellular Ca(2+) concentration, and bursting electrical activity. The mechanisms that maintain an oscillatory response are not fully understood, yet several models have been proposed. Only some can account for experiments supporting that metabolism is intrinsically oscillatory in β-cells. The dual oscillator model (DOM) implicates glycolysis as the source of oscillatory metabolism. In the companion article, we use recently developed biosensors to confirm that glycolysis is oscillatory and further elucidate the coordination of metabolic and electrical signals in the insulin secretory pathway. In this report, we modify the DOM by incorporating an established link between metabolism and intracellular Ca(2+) to reconcile model predictions with experimental observations from the companion article. With modification, we maintain the distinguishing feature of the DOM, oscillatory glycolysis, but introduce the ability of Ca(2+) influx to reshape glycolytic oscillations by promoting glycolytic efflux. We use the modified model to explain measurements from the companion article and from previously published experiments with islets.
Copyright © 2016 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Weigle D.S. Pulsatile secretion of fuel-regulatory hormones. Diabetes. 1987;36:764–775. - PubMed
-
- Bertram R., Sherman A., Satin L.S. Metabolic and electrical oscillations: partners in controlling pulsatile insulin secretion. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007;293:E890–E900. - PubMed
-
- Meier J.J., Veldhuis J.D., Butler P.C. Pulsatile insulin secretion dictates systemic insulin delivery by regulating hepatic insulin extraction in humans. Diabetes. 2005;54:1649–1656. - PubMed
-
- Bratusch-Marrain P.R., Komjati M., Waldhäusl W.K. Efficacy of pulsatile versus continuous insulin administration on hepatic glucose production and glucose utilization in type I diabetic humans. Diabetes. 1986;35:922–926. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

