Nonadherence to Antihypertensive Medication Among Hypertensive Adults in the United States─HealthStyles, 2010
- PMID: 26841710
- PMCID: PMC4991960
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.12786
Nonadherence to Antihypertensive Medication Among Hypertensive Adults in the United States─HealthStyles, 2010
Abstract
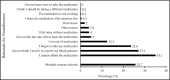
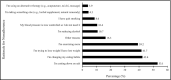
Nonadherence, or not taking medications as prescribed, to antihypertensive medications has been associated with uncontrolled hypertension. The authors analyzed data from HealthStyles 2010 to assess medication nonadherence among adults with hypertension. The overall prevalence of hypertension was 27.4% and the prevalence of nonadherence was 30.5% among hypertensive adult respondents. Nonadherence rates were highest among younger adults (aged 18-44 years), Hispanics, those who reported lowest annual income (<$25,000), and those who reported depression. The most common reason stated for nonadherence was "I cannot afford the medication" (35.1%). A multivariate logistic regression model showed age, race, and household income to be associated with nonadherence. These findings suggest that certain subgroups are more likely to report barriers to adherence. Interventions to support the management of hypertension should consider the identification of certain at-risk subgroups and utilize community and clinical evidenced-based resources to improve long-term control.
Published 2016. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decoding Nonadherence to Hypertensive Medication in New York City: A Population Segmentation Approach.J Prim Care Community Health. 2019 Jan-Dec;10:2150132719829311. doi: 10.1177/2150132719829311. J Prim Care Community Health. 2019. PMID: 30767604 Free PMC article.
-
National Rates of Nonadherence to Antihypertensive Medications Among Insured Adults With Hypertension, 2015.Hypertension. 2019 Dec;74(6):1324-1332. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.13616. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Hypertension. 2019. PMID: 31679429
-
Barriers to antihypertensive medication adherence among adults--United States, 2005.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2008 Dec;10(12):922-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2008.00049.x. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2008. PMID: 19120718 Free PMC article.
-
Medication nonadherence: an unrecognized cardiovascular risk factor.MedGenMed. 2007 Sep 19;9(3):58. MedGenMed. 2007. PMID: 18092064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nonadherence in Hypertension: How to Develop and Implement Chemical Adherence Testing.Hypertension. 2022 Jan;79(1):12-23. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.17596. Epub 2021 Nov 5. Hypertension. 2022. PMID: 34739765 Review.
Cited by
-
Association Between Health Literacy and Medication Adherence Among Hispanics with Hypertension.J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2019 Jun;6(3):517-524. doi: 10.1007/s40615-018-00550-z. Epub 2019 Jan 3. J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2019. PMID: 30607576 Free PMC article.
-
Use of strategies to improve antihypertensive medication adherence within United States outpatient health care practices, DocStyles 2015-2016.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2018 Feb;20(2):225-232. doi: 10.1111/jch.13188. Epub 2018 Feb 4. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2018. PMID: 29397582 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of a Culturally and Linguistically Competent Community Health Coach Intervention for Chinese with Hypertension.Asian Pac Isl Nurs J. 2020;5(3):111-119. doi: 10.31372/20200503.1087. Asian Pac Isl Nurs J. 2020. PMID: 33324728 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of a Culturally Tailored mHealth Medication Regimen Self-Management Program upon Blood Pressure among Hypertensive Hispanic Adults.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Apr 6;16(7):1226. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16071226. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 30959858 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Out-of-pocket costs and adherence to antihypertensive agents among older adults covered by the public drug insurance plan in Quebec.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2017 Sep 8;11:1513-1522. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S138364. eCollection 2017. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2017. PMID: 28932106 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nwankwo T, Yoon SS, Burt V, et al. Hypertension among adults in the United States: national health and nutrition examination survey, 2011–2012. NCHS Data Brief. 2013;133:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Egan BM, Zhao Y, Axon RN. US trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension, 1988–2008. JAMA. 2010;303:2043–2050. - PubMed
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris G, Black HR, et al. Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension. 2003;42:1206–1252. - PubMed
-
- Sanson‐Fisher RW, Clover K. Compliance in the treatment of hypertension. A need for action. Am J Hypertens. 1995;8:82S–88S. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical