Oxidised palm oil and sucrose induced hyperglycemia in normal rats: effects of Sclerocarya birrea stem barks aqueous extract
- PMID: 26841874
- PMCID: PMC4739403
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-016-1009-0
Oxidised palm oil and sucrose induced hyperglycemia in normal rats: effects of Sclerocarya birrea stem barks aqueous extract
Abstract
Background: Consumption of foods rich in carbohydrates and fats, result in an increase in obesity and consequently type 2 diabetes. The present study was carried out to evaluate the effects of oxidised palm oil and sucrose (SOPO +S) on some metabolic parameters and to investigate the effects of aqueous extract from barks of Sclerocarrya birrea on SOPO + S induced damages.
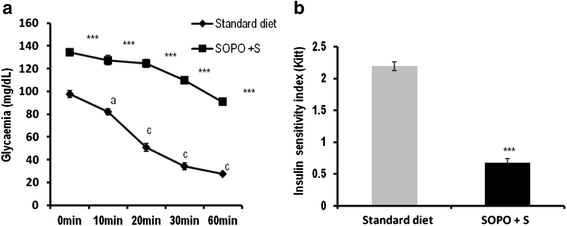
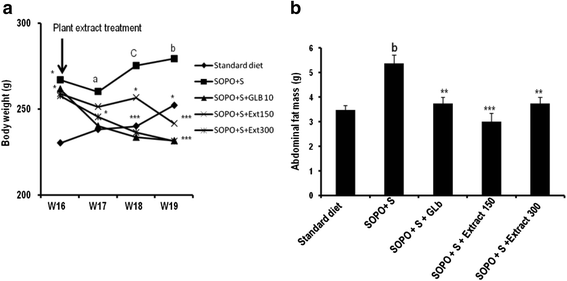
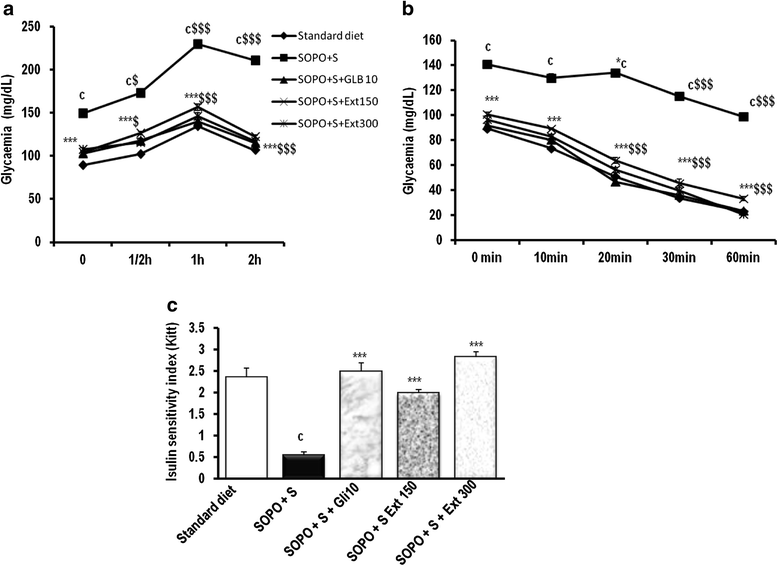
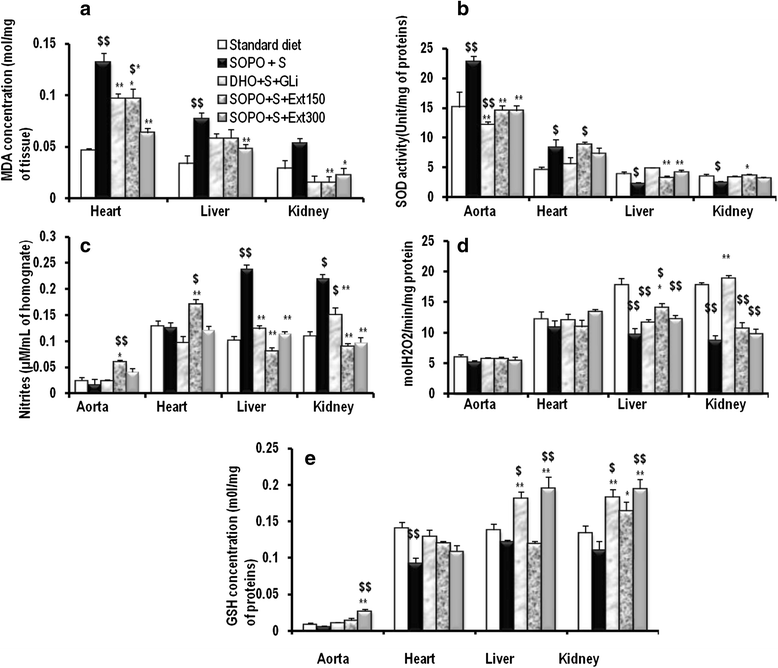
Methods: During 16 weeks, animals received every day a supplement of oxidised palm oil (10 %) and 10 % sucrose as drinking water). Control rat received standard diet and drinking water without sucrose. At the end of this period, animal presenting intolerance in glucose test and insensitivity to insulin were continuously feed with hypercaloric diet along with the administration of the plant extract (150 or 300 mg/kg) or glibenclamide (10 mg/kg) during three weeks. OGTT was performed; insulin sensitivity was assessed by performing insulin tolerance test and determining insulin sensitivity index (Kitt). Several parameters were evaluated including body weight, abdominal fat mass, blood glucose levels, blood pressure, serum lipid profile, and serum transaminases (ALT and AST). Oxidative parameters were measured by MDA levels, nitrites levels, SOD levels, reduced glutathione content and by enzyme activities of SOD and catalase.
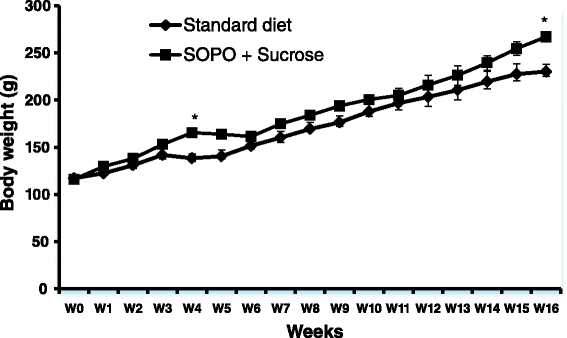
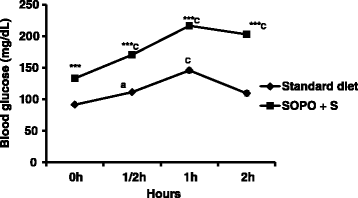
Results: Animal receiving a supplement of oxidised palm oil and sucrose showed hyperglycaemia, glucose intolerance, insulin resistance and a significant increase in body weight and abdominal fat mass compared to normal rats. In addition, there was a significant increase of SOD in aorta and heart, nitrites in liver and kidney, malondialdehyde (MDA) in heart, liver and kidney. It was also observed a significant reduction in the activities of the SOD and catalase in liver, kidney and reduced glutathione levels in heart. Concomitant treatment of plant extract with SOPO + S brought glycaemia and blood pressure towards normal value, restored glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. The plant extract prevent the increase or decrease in the activity of the enzyme depending to the organ, reduced MDA and nitrites levels.
Conclusion: These results highlighted the hyperglycaemic and oxidant character of SOPO + S diet and confirm the hypoglycaemic, and antioxidant action of sclerocarya birrea aqueous extract in diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the analgesic, anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic properties of Sclerocarya birrea (A. Rich.) Hochst. stem-bark aqueous extract in mice and rats.Phytother Res. 2004 Aug;18(8):601-8. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1503. Phytother Res. 2004. PMID: 15476310
-
Hypoglycemic effect of Sclerocarya birrea [(A. Rich.) Hochst.] [Anacardiaceae] stem-bark aqueous extract in rats.Phytomedicine. 2003 Nov;10(8):675-81. doi: 10.1078/0944-7113-00295. Phytomedicine. 2003. PMID: 14692729
-
Sclerocarya birrea (Anacardiaceae) stem-bark extract corrects glycaemia in diabetic rats and acts on beta-cells by enhancing glucose-stimulated insulin secretion.J Endocrinol. 2010 Apr;205(1):79-86. doi: 10.1677/JOE-09-0311. Epub 2010 Jan 8. J Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20061513
-
Effect of Sclerocarya birrea (Anacardiaceae) stem bark methylene chloride/methanol extract on streptozotocin-diabetic rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2007 Apr 4;110(3):434-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.10.020. Epub 2006 Oct 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17141993
-
SUCROSE INTOLERANCE: AN ENZYMATIC DEFECT.Nutr Rev. 1965 Apr;23:101-2. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1965.tb02095.x. Nutr Rev. 1965. PMID: 14267995 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Hydroethanolic Extract from Bridelia atroviridis Müll. Arg. Bark Improves Haematological and Biochemical Parameters in Nicotinamide-/Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Nov 25;2020:3160834. doi: 10.1155/2020/3160834. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 33293987 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Extracts for Type 2 Diabetes: From Traditional Medicine to Modern Drug Discovery.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jan 9;10(1):81. doi: 10.3390/antiox10010081. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33435282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential of fruit ethanolic extract Etlingera hemisphaerica as a solution for hyperglycemia, uremia, and hypercreatininemia in mice (Mus musculus).Open Vet J. 2024 Dec;14(12):3296-3308. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2024.v14.i12.14. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Open Vet J. 2024. PMID: 39927360 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Antidiabetic Compounds from the Aqueous Extract of Sclerocarya birrea Leaves.Molecules. 2022 Nov 21;27(22):8095. doi: 10.3390/molecules27228095. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36432195 Free PMC article.
-
From Diabetes Care to Heart Failure Management: A Potential Therapeutic Approach Combining SGLT2 Inhibitors and Plant Extracts.Nutrients. 2022 Sep 10;14(18):3737. doi: 10.3390/nu14183737. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36145112 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bastard JP, Maachi M, Lagathu C, Kim MJ, Caron M. Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Cytokine Network. 2006;17:4–12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

