A combination of traditional learning and e-learning can be more effective on radiological interpretation skills in medical students: a pre- and post-intervention study
- PMID: 26842495
- PMCID: PMC4739398
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-016-0569-5
A combination of traditional learning and e-learning can be more effective on radiological interpretation skills in medical students: a pre- and post-intervention study
Abstract
Background: The ability to interpret an X-Ray is a vital skill for graduating medical students which guides clinicians towards accurate diagnosis and treatment of the patient. However, research has suggested that radiological interpretation skills are less than satisfactory in not only medical students, but also in residents and consultants.
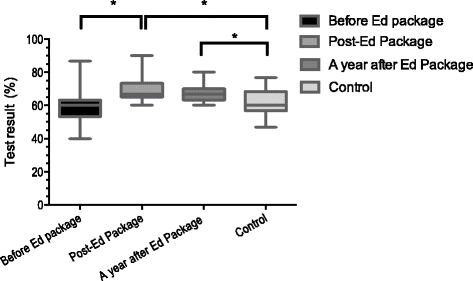
Methods: This study investigated the effectiveness of e-learning for the development of X-ray interpretation skills in pre-clinical medical students. Competencies in clinical X-Ray interpretation were assessed by comparison of pre- and post-intervention scores and one year follow up assessment, where the e-learning course was the 'intervention'.
Results: Our results demonstrate improved knowledge and skills in X-ray interpretation in students. Assessment of the post training students showed significantly higher scores than the scores of control group of students undertaking the same assessment at the same time.
Conclusions: The development of the Internet and advances in multimedia technologies has paved the way for computer-assisted education. As more rural clinical schools are established the electronic delivery of radiology teaching through websites will become a necessity. The use of e-learning to deliver radiology tuition to medical students represents an exciting alternative and is an effective method of developing competency in radiological interpretation for medical students.
Figures
Similar articles
-
E-learning for chest x-ray interpretation improves medical student skills and confidence levels.BMC Med Educ. 2018 Nov 12;18(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s12909-018-1364-2. BMC Med Educ. 2018. PMID: 30419883 Free PMC article.
-
Development and evaluation of methodologies for teaching focused cardiac ultrasound skills to medical students.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2014 Mar;27(3):302-9. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2013.12.006. Epub 2014 Jan 13. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2014. PMID: 24433979
-
Interpretation of radiological images: towards a framework of knowledge and skills.Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2014 Oct;19(4):565-80. doi: 10.1007/s10459-013-9488-y. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2014. PMID: 24449126 Review.
-
Training and assessment of CXR/basic radiology interpretation skills: results from the 2005 CDIM Survey.Teach Learn Med. 2008 Apr-Jun;20(2):157-62. doi: 10.1080/10401330801991840. Teach Learn Med. 2008. PMID: 18444203
-
A review of peer-assisted learning to deliver interprofessional supplementary image interpretation skills.Radiography (Lond). 2017 Sep;23 Suppl 1:S64-S69. doi: 10.1016/j.radi.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 May 24. Radiography (Lond). 2017. PMID: 28780955 Review.
Cited by
-
Educating the next generation of radiologists: a comparative report of ChatGPT and e-learning resources.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2024 May 13;30(3):163-174. doi: 10.4274/dir.2023.232496. Epub 2023 Dec 25. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38145370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improved self- and external assessment of the clinical abilities of medical students through structured improvement measures in an internal medicine bedside course.GMS J Med Educ. 2016 Aug 15;33(4):Doc59. doi: 10.3205/zma001058. eCollection 2016. GMS J Med Educ. 2016. PMID: 27579359 Free PMC article.
-
Blending electronic techniques with traditional teaching methods to enhance chest X-ray interpretation in medical students.PLoS One. 2025 Aug 6;20(8):e0328159. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328159. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40768399 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Undergraduate medical education amid COVID-19: a qualitative analysis of enablers and barriers to acquiring competencies in distant learning using focus groups.Med Educ Online. 2021 Dec;26(1):1940765. doi: 10.1080/10872981.2021.1940765. Med Educ Online. 2021. PMID: 34128776 Free PMC article.
-
Serial image interpretation tasks improve accuracy and increase confidence in Level 1 echocardiography reporting: a pilot study.Echo Res Pract. 2023 Apr 6;10(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s44156-023-00018-9. Echo Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37020250 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

