Haloperidol Suppresses NF-kappaB to Inhibit Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Response in RAW 264 Cells
- PMID: 26842661
- PMCID: PMC4747317
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.895739
Haloperidol Suppresses NF-kappaB to Inhibit Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Response in RAW 264 Cells
Abstract
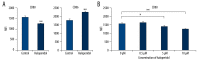
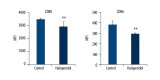
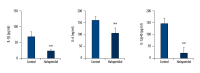
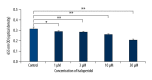
BACKGROUND Haloperidol, a tranquilizing agent, is administered both to treat symptoms of psychotic disorders and to sedate agitated and delirious patients. Notably, haloperidol has been suggested to inhibit the immune response through unknown mechanisms. We hypothesized that the sedative modulates the immune response via NF-κB. MATERIAL AND METHODS Using flow cytometry, we analyzed the effects of haloperidol on expression CD80 and CD86 in RAW 264 cells and in primary macrophages derived from bone marrow. Secretion of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and IL-12 p40 was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. In addition, NF-κB activation was evaluated using a reporter assay based on secretory embryonic alkaline phosphatase. Finally, synthetic antagonists were used to identify the dopamine receptor that mediates the effects of haloperidol. RESULTS Haloperidol inhibited NF-κB activation, and thereby suppressed expression of CD80, as well as secretion of IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-12 p40. CD80 and IL-6 levels were similarly attenuated by a D2-like receptor antagonist, but not by a D1-like receptor antagonist. CONCLUSIONS The data strongly suggest that haloperidol inhibits the immune response by suppressing NF-kB signaling via the dopamine D2 receptor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Gingerol on Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells by Inhibiting NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Inflammation. 2018 Jun;41(3):835-845. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0737-3. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 29508185
-
Nauclea officinalis inhibits inflammation in LPS-mediated RAW 264.7 macrophages by suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 May 13;183:159-165. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.01.018. Epub 2016 Jan 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26806575
-
DXXK exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-κB/COX-2 signalling pathway and the expression of inflammatory mediators.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Feb 3;178:199-208. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.11.016. Epub 2015 Nov 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26571085
-
Haloperidol suppresses murine dendritic cell maturation and priming of the T helper 1-type immune response.Anesth Analg. 2015 Apr;120(4):895-902. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000606. Anesth Analg. 2015. PMID: 25627077
-
Lupeol inhibits LPS-induced NF-kappa B signaling in intestinal epithelial cells and macrophages, and attenuates acute and chronic murine colitis.Life Sci. 2016 Feb 1;146:100-8. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.01.001. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26767626
Cited by
-
Dopamine, Immunity, and Disease.Pharmacol Rev. 2023 Jan;75(1):62-158. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.122.000618. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Pharmacol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36757901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Macrophage Dopamine Receptors in Mediating Cytokine Production: Implications for Neuroinflammation in the Context of HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019 Mar;14(1):134-156. doi: 10.1007/s11481-018-9825-2. Epub 2018 Dec 5. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30519866 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Haloperidol use and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis.MedComm Futur Med. 2023 Dec;2(4):10.1002/mef2.66. doi: 10.1002/mef2.66. Epub 2023 Nov 24. MedComm Futur Med. 2023. PMID: 38298936 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Peripheral Blood Leukocyte RNA-Seq Identifies a Set of Genes Related to Abnormal Psychomotor Behavior Characteristics in Patients with Schizophrenia.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Feb 10;26:e922426. doi: 10.12659/MSM.922426. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32038049 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-oxidant and degenerative effects of haloperidol under inflammatory conditions in rat; the involvement of SIRT1 and NF-κB signaling pathways.Vet Res Forum. 2021 Spring;12(2):175-183. doi: 10.30466/vrf.2019.105811.2514. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Vet Res Forum. 2021. PMID: 34345383 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singer AJ, Clark RA. Cutaneous wound healing. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:738–46. - PubMed
-
- Riker RR, Shehabi Y, Bokesch PM, et al. Dexmedetomidine vs. midazolam for sedation of critically ill patients: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2009;301:489–99. - PubMed
-
- Yang SY, Liao YT, Liu HC, et al. Antipsychotic drugs, mood stabilizers, and risk of pneumonia in bipolar disorder: a nationwide case-control study. J Clin Psychiatry. 2013;74:e79–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

