Aurora kinase targeting in lung cancer reduces KRAS-induced transformation
- PMID: 26842935
- PMCID: PMC4739397
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-016-0494-6
Aurora kinase targeting in lung cancer reduces KRAS-induced transformation
Erratum in
-
Correction: Aurora kinase targeting in lung cancer reduces KRAS-induced transformation.Mol Cancer. 2024 Mar 9;23(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-01964-6. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38461274 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
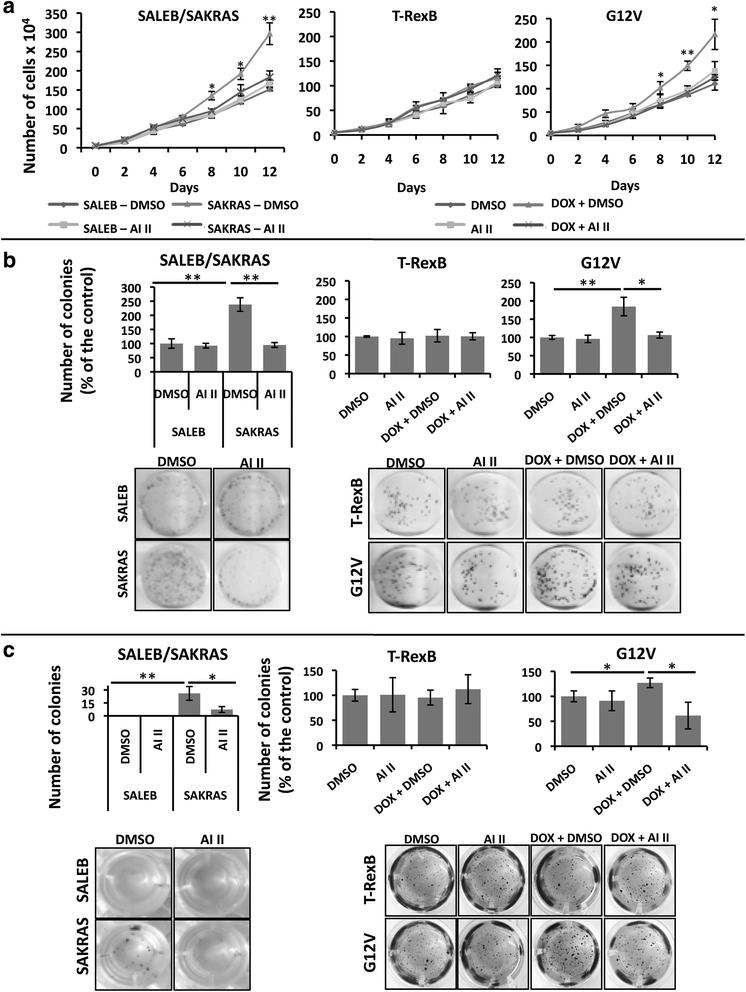
Background: Activating mutations in KRAS are prevalent in lung cancer and have been causally linked to the oncogenic process. However, therapies targeted to oncogenic RAS have been ineffective to date and identification of KRAS targets that impinge on the oncogenic phenotype is warranted. Based on published studies showing that mitotic kinases Aurora A (AURKA) and B (AURKB) cooperate with oncogenic RAS to promote malignant transformation and that AURKA phosphorylates RAS effector pathway components, the aim of this study was to investigate whether AURKA and AURKB are KRAS targets in lung cancer and whether targeting these kinases might be therapeutically beneficial.
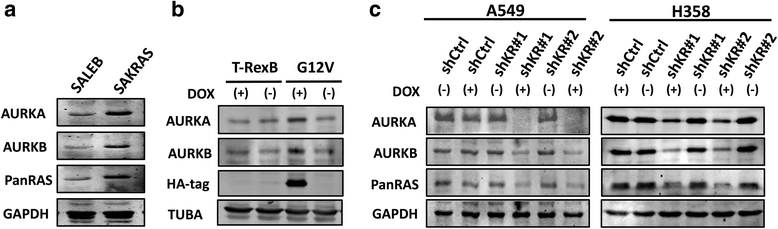
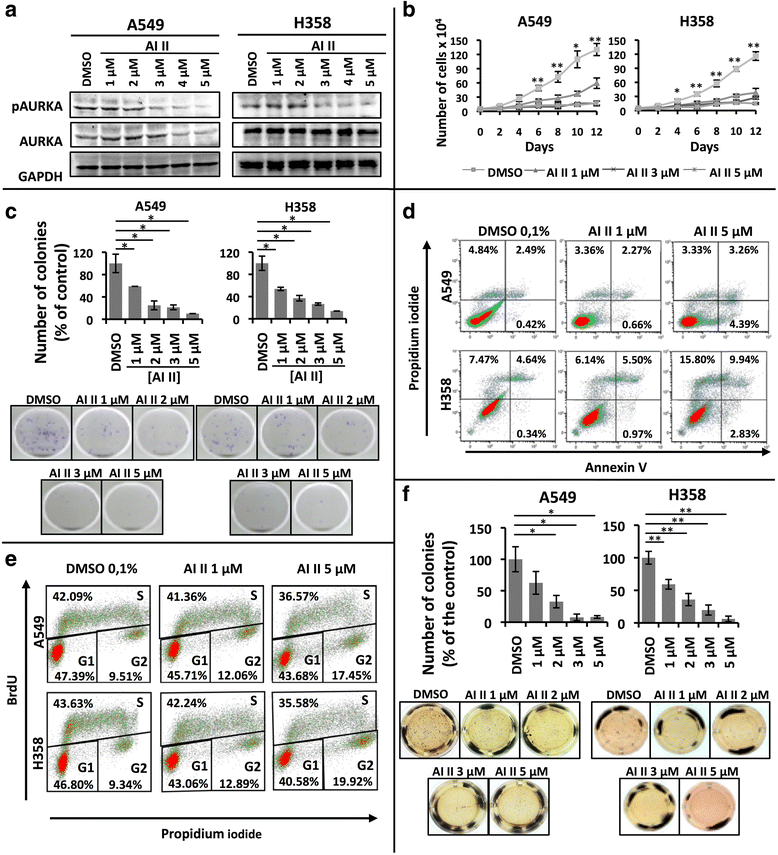
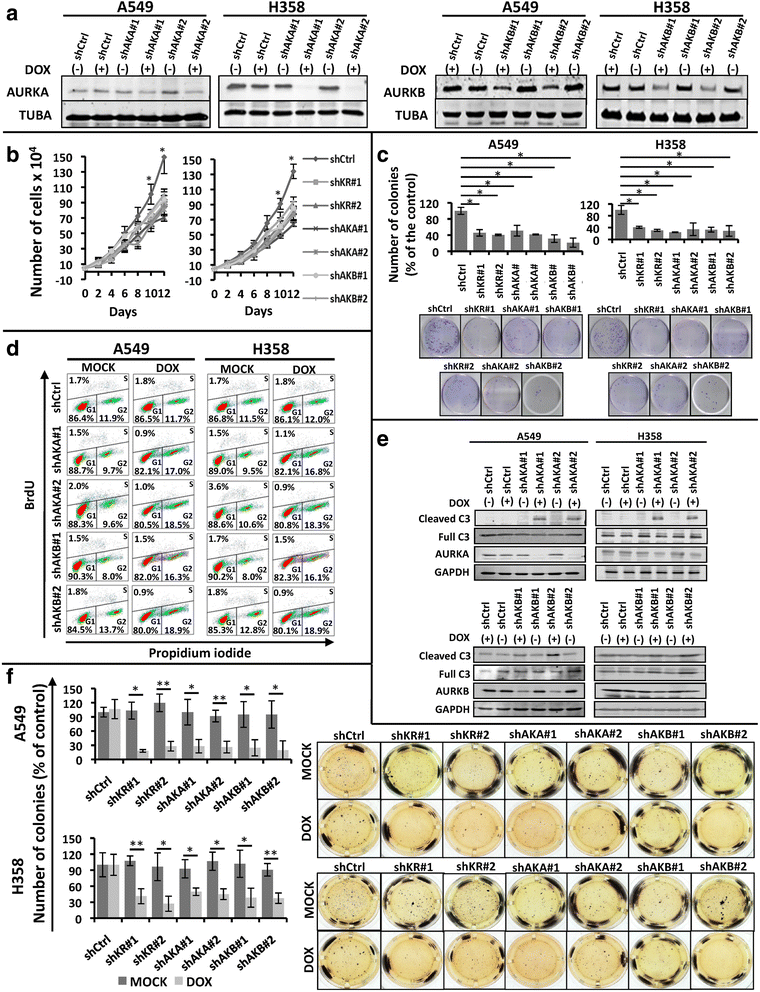
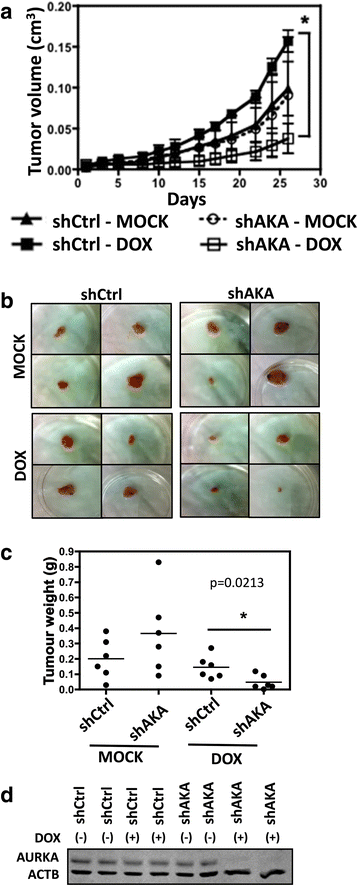
Methods: In order to determine whether oncogenic KRAS induces Aurora kinase expression, we used qPCR and western blotting in three different lung cell-based models of gain- or loss-of-function of KRAS. In order to determine the functional role of these kinases in KRAS-induced transformation, we generated KRAS-positive A549 and H358 cells with stable and inducible shRNA-mediated knockdown of AURKA or AURKB and evaluated transformation in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. In order to validate AURKA and/or AURKB as therapeutically relevant KRAS targets in lung cancer, we treated A549 and H358 cells, as well as two different lung cell based models of gain-of-function of KRAS with a dual Aurora kinase inhibitor and performed functional in vitro assays.
Results: We determined that KRAS positively regulates AURKA and AURKB expression. Furthermore, in KRAS-positive H358 and A549 cell lines, inducible knockdown of AURKA or AURKB, as well as treatment with a dual AURKA/AURKB inhibitor, decreased growth, viability, proliferation, transformation, and induced apoptosis in vitro. In addition, inducible shRNA-mediated knockdown of AURKA in A549 cells decreased tumor growth in vivo. More importantly, dual pharmacological inhibiton of AURKA and AURKB reduced growth, viability, transformation, and induced apoptosis in vitro in an oncogenic KRAS-dependent manner, indicating that Aurora kinase inhibition therapy can specifically target KRAS-transformed cells.
Conclusions: Our results support our hypothesis that Aurora kinases are important KRAS targets in lung cancer and suggest Aurora kinase inhibition as a novel approach for KRAS-induced lung cancer therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of AURKA Reduces Proliferation and Survival of Gastrointestinal Cancer Cells With Activated KRAS by Preventing Activation of RPS6KB1.Gastroenterology. 2019 Feb;156(3):662-675.e7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.10.030. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 30342037 Free PMC article.
-
Aurora A kinase and its activator TPX2 are potential therapeutic targets in KRAS-induced pancreatic cancer.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020 Jun;43(3):445-460. doi: 10.1007/s13402-020-00498-5. Epub 2020 Mar 19. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020. PMID: 32193808
-
Daurinol Enhances the Efficacy of Radiotherapy in Lung Cancer via Suppression of Aurora Kinase A/B Expression.Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Jul;14(7):1693-704. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0960. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 25882311
-
Aurora Kinase B Inhibition: A Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Cancer.Molecules. 2021 Apr 1;26(7):1981. doi: 10.3390/molecules26071981. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33915740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitotic syndicates Aurora Kinase B (AURKB) and mitotic arrest deficient 2 like 2 (MAD2L2) in cohorts of DNA damage response (DDR) and tumorigenesis.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2021 Jan-Jun;787:108376. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2021.108376. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2021. PMID: 34083040 Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying General Tumor and Specific Lung Cancer Biomarkers by Transcriptomic Analysis.Biology (Basel). 2022 Jul 20;11(7):1082. doi: 10.3390/biology11071082. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36101460 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of AURKA Reduces Proliferation and Survival of Gastrointestinal Cancer Cells With Activated KRAS by Preventing Activation of RPS6KB1.Gastroenterology. 2019 Feb;156(3):662-675.e7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.10.030. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 30342037 Free PMC article.
-
The Identification of Key Gene Expression Signature and Biological Pathways in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma.J Cancer. 2020 Jan 16;11(7):1712-1726. doi: 10.7150/jca.38379. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32194783 Free PMC article.
-
Alisertib exerts KRAS allele‑specific anticancer effects on colorectal cancer cell lines.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Apr 11;25(6):243. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.11942. eCollection 2023 Jun. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37153900 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear localisation of Aurora-A: its regulation and significance for Aurora-A functions in cancer.Oncogene. 2021 Jun;40(23):3917-3928. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01766-w. Epub 2021 May 13. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 33981003 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

