The downregulation of the RNA-binding protein Staufen2 in response to DNA damage promotes apoptosis
- PMID: 26843428
- PMCID: PMC4856980
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw057
The downregulation of the RNA-binding protein Staufen2 in response to DNA damage promotes apoptosis
Abstract
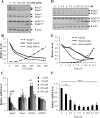
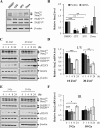
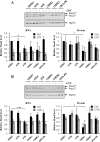
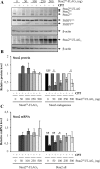
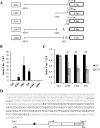
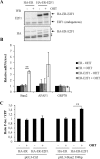
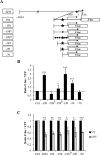
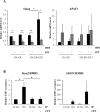
Staufen2 (Stau2) is an RNA-binding protein involved in cell fate decision by controlling several facets of mRNA processing including localization, splicing, translation and stability. Herein we report that exposure to DNA-damaging agents that generate replicative stress such as camptothecin (CPT), 5-fluoro-uracil (5FU) and ultraviolet radiation (UVC) causes downregulation of Stau2 in HCT116 colorectal cancer cells. In contrast, other agents such as doxorubicin and ionizing radiation had no effect on Stau2 expression. Consistently, Stau2 expression is regulated by the ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR) signaling pathway but not by the DNA-PK or ataxia telangiectasia mutated/checkpoint kinase 2 pathways. Stau2 downregulation is initiated at the level of transcription, independently of apoptosis induction. Promoter analysis identified a short 198 bp region which is necessary and sufficient for both basal and CPT-regulated Stau2 expression. The E2F1 transcription factor regulates Stau2 in untreated cells, an effect that is abolished by CPT treatment due to E2F1 displacement from the promoter. Strikingly, Stau2 downregulation enhances levels of DNA damage and promotes apoptosis in CPT-treated cells. Taken together our results suggest that Stau2 is an anti-apoptotic protein that could be involved in DNA replication and/or maintenance of genome integrity and that its expression is regulated by E2F1 via the ATR signaling pathway.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Roos W.P., Kaina B. DNA damage-induced cell death: from specific DNA lesions to the DNA damage response and apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2013;332:237–248. - PubMed
-
- Medema R.H., Macurek L. Checkpoint control and cancer. Oncogene. 2012;31:2601–2613. - PubMed
-
- Aziz K., Nowsheen S., Pantelias G., Iliakis G., Gorgoulis V.G., Georgakilas A.G. Targeting DNA damage and repair: embracing the pharmacological era for successful cancer therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012;133:334–350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

