RNA cleavage products generated by antisense oligonucleotides and siRNAs are processed by the RNA surveillance machinery
- PMID: 26843429
- PMCID: PMC4838368
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw065
RNA cleavage products generated by antisense oligonucleotides and siRNAs are processed by the RNA surveillance machinery
Abstract
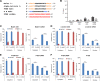
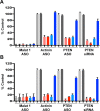
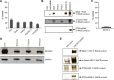
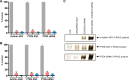
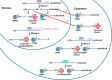
DNA-based antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) elicit cleavage of the targeted RNA by the endoribonuclease RNase H1, whereas siRNAs mediate cleavage through the RNAi pathway. To determine the fates of the cleaved RNA in cells, we lowered the levels of the factors involved in RNA surveillance prior to treating cells with ASOs or siRNA and analyzed cleavage products by RACE. The cytoplasmic 5' to 3' exoribonuclease XRN1 was responsible for the degradation of the downstream cleavage products generated by ASOs or siRNA targeting mRNAs. In contrast, downstream cleavage products generated by ASOs targeting nuclear long non-coding RNA Malat 1 and pre-mRNA were degraded by nuclear XRN2. The downstream cleavage products did not appear to be degraded in the 3' to 5' direction as the majority of these products contained intact poly(A) tails and were bound by the poly(A) binding protein. The upstream cleavage products of Malat1 were degraded in the 3' to 5' direction by the exosome complex containing the nuclear exoribonuclease Dis3. The exosome complex containing Dis3 or cytoplasmic Dis3L1 degraded mRNA upstream cleavage products, which were not bound by the 5'-cap binding complex and, consequently, were susceptible to degradation in the 5' to 3' direction by the XRN exoribonucleases.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


References
-
- Badis G., Saveanu C., Fromont-Racine M., Jacquier A. Targeted mRNA degradation by deadenylation-independent decapping. Mol. Cell. 2004;15:5–15. - PubMed
-
- Conti E., Izaurralde E. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: molecular insights and mechanistic variations across species. Curr. Opin. Cell Boil. 2005;17:316–325. - PubMed
-
- Parker R., Song H. The enzymes and control of eukaryotic mRNA turnover. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004;11:121–127. - PubMed
-
- Garneau N.L., Wilusz J., Wilusz C.J. The highways and byways of mRNA decay. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007;8:113–126. - PubMed
-
- Goldstrohm A.C., Wickens M. Multifunctional deadenylase complexes diversify mRNA control. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008;9:337–344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

