Neurofascin-155 IgG4 in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
- PMID: 26843559
- PMCID: PMC4793783
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002418
Neurofascin-155 IgG4 in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
Abstract
Objective: We report the clinical and serologic features of Japanese patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) displaying anti-neurofascin-155 (NF155) immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) antibodies.
Methods: In sera from 533 patients with CIDP, anti-NF155 IgG4 antibodies were detected by ELISA. Binding of IgG antibodies to central and peripheral nerves was tested.
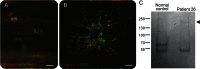
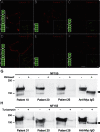
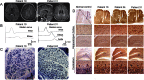
Results: Anti-NF155 IgG4 antibodies were identified in 38 patients (7%) with CIDP, but not in disease controls or normal participants. These patients were younger at onset as compared to 100 anti-NF155-negative patients with CIDP. Twenty-eight patients (74%) presented with sensory ataxia, 16 (42%) showed tremor, 5 (13%) presented with cerebellar ataxia associated with nystagmus, 3 (8%) had demyelinating lesions in the CNS, and 20 of 25 (80%) had poor response to IV immunoglobulin. The clinical features of the antibody-positive patients were statistically more frequent as compared to negative patients with CIDP (n = 100). Anti-NF155 IgG antibodies targeted similarly central and peripheral paranodes.
Conclusion: Anti-NF155 IgG4 antibodies were associated with a subgroup of patients with CIDP showing a younger age at onset, ataxia, tremor, CNS demyelination, and a poor response to IV immunoglobulin. The autoantibodies may serve as a biomarker to improve patients' diagnosis and guide treatments.
© 2016 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Close to the node but far enough: What nodal antibodies tell us about CIDP and its therapies.Neurology. 2016 Mar 1;86(9):796-7. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002427. Epub 2016 Feb 3. Neurology. 2016. PMID: 26843563 No abstract available.
References
-
- Latov N. Diagnosis and treatment of chronic acquired demyelinating polyneuropathies. Nat Rev Neurol 2014;10:435–446. - PubMed
-
- Charles P, Tait S, Faivre-Sarrailh C, et al. Neurofascin is a glial receptor for the paranodin/Caspr-contactin axonal complex at the axoglial junction. Curr Biol 2002;12:217–220. - PubMed
-
- Bhat MA, Rios JC, Lu Y, et al. Axon-glia interactions and the domain organization of myelinated axons require neurexin IV/Caspr/paranodin. Neuron 2001;30:369–383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
