Agreement of objectively measured physical activity and sedentary time in preschool children
- PMID: 26844129
- PMCID: PMC4721440
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2015.07.009
Agreement of objectively measured physical activity and sedentary time in preschool children
Abstract
Objective: To determine the intra-individual agreement for objectively measured physical activity (PA) and sedentary behavior (SED) over two subsequent weeks in preschool children.
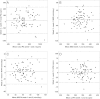
Method: Ninety-one children aged 3 to 5 years (49% boys) from three preschools in Sogn og Fjordane, Norway, provided 14 consecutive days of accelerometer data (Actigraph GT3X +) during the autumn of 2014. Week-by-week reliability was assessed using intraclass correlation (ICC), Bland-Altman plots and 95% limits of agreement for different wear time criteria (≥ 6, 8 and 10 h/day and ≥ 3 and 5 days/week).
Results: The week-by-week ICC was ≥ 0.75 for all variables across all wear criteria applied, except for absolute sedentary time (ICC 0.61-0.81). Using a ≥ 8 h/day and ≥ 3 days/week criterion (n = 78), limits of agreement were ± 209.5 cpm for overall PA, ± 68.6 min/day for SED, ± 43.8 min/day for light PA, ± 20.2 min/day for moderate-to-vigorous PA, and ± 55.9 min/day for light-to-vigorous PA, equaling 1.0-1.6 standard deviation units.
Conclusion: Considerable week-by-week variability was found for all variables. Researchers need to be aware of substantial intra-individual variability in accelerometer-measurements and take necessary actions according to the hypothesis under study, as noise in any measurement will preclude researchers' ability to arrive at valid conclusions in epidemiology.
Keywords: Accelerometry; Bland–Altman plot; Measurement; Test–retest.
Figures
References
-
- Addy C.L., Trilk J.L., Dowda M., Byun W., Pate R.R. Assessing preschool children's physical activity: how many days of accelerometry measurement. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2014;26:103–109. - PubMed
-
- Basterfield L., Adamson A.J., Pearce M.S., Reilly J.J. Stability of habitual physical activity and sedentary behavior monitoring by accelerometry in 6-to 8-year-olds. J. Phys. Act. Health. 2011;8:543–547. - PubMed
-
- Bland J.M., Altman D.G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986;1:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Bornstein D.B., Beets M.W., Byun W., McIver K. Accelerometer-derived physical activity levels of preschoolers: a meta-analysis. J. Sci. Med. Sport. 2011;14:504–511. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

