Radiation-induced CD8 T-lymphocyte Apoptosis as a Predictor of Breast Fibrosis After Radiotherapy: Results of the Prospective Multicenter French Trial
- PMID: 26844275
- PMCID: PMC4703704
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.10.024
Radiation-induced CD8 T-lymphocyte Apoptosis as a Predictor of Breast Fibrosis After Radiotherapy: Results of the Prospective Multicenter French Trial
Abstract
Background: Monocentric cohorts suggested that radiation-induced CD8 T-lymphocyte apoptosis (RILA) can predict late toxicity after curative intent radiotherapy (RT). We assessed the role of RILA as a predictor of breast fibrosis (bf +) after adjuvant breast RT in a prospective multicenter trial.
Methods: A total of 502 breast-cancer patients (pts) treated by conservative surgery and adjuvant RT were recruited at ten centers. RILA was assessed before RT by flow cytometry. Impact of RILA on bf + (primary endpoint) or relapse was assessed using a competing risk method. Receiver-operator characteristic (ROC) curve analyses were also performed in intention to treat. This study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT00893035 and final analyses are presented here.
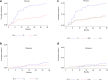
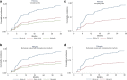
Findings: Four hundred and fifty-six pts (90.8%) were included in the final analysis. One hundred and eight pts (23.7%) received whole breast and node irradiation. A boost dose of 10-16 Gy was delivered in 449 pts (98.5%). Adjuvant hormonotherapy was administered to 349 pts (76.5%). With a median follow-up of 38.6 months, grade ≥ 2 bf + was observed in 64 pts (14%). A decreased incidence of grade ≥ 2 bf + was observed for increasing values of RILA (p = 0.012). No grade 3 bf + was observed for patients with RILA ≥ 12%. The area under the ROC curve was 0.62. For cut-off values of RILA ≥ 20% and < 12%, sensitivity and specificity were 80% and 34%, 56% and 67%, respectively. Negative predictive value for grade ≥ 2 bf + was equal to 91% for RILA ≥ 20% and positive predictive value was equal to 22% for RILA < 12% where the overall prevalence of grade ≥ 2 bf + was estimated at 14%. A significant decrease in the risk of grade ≥ 2 bf + was found if patients had no adjuvant hormonotherapy (sHR = 0.31, p = 0.007) and presented a RILA ≥ 12% (sHR = 0.45, p = 0.002).
Interpretation: RILA significantly predicts the risk of breast fibrosis. This study validates the use of RILA as a rapid screening test before RT delivery and will change definitely our daily clinical practice in radiation oncology.
Funding: The French National Cancer Institute (INCa) through the "Program Hospitalier de Recherche Clinique (PHRC)".
Keywords: Apoptosis; Breast fibrosis; Lymphocyte; Prediction; Radiotherapy.
Figures

Comment in
-
Radiation Induced Lymphocyte Apoptosis: An Effective Way of "Tailoring" Radiotherapy to the Right Patients Only?EBioMedicine. 2015 Nov 7;2(12):1852-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.11.014. eCollection 2015 Dec. EBioMedicine. 2015. PMID: 26844256 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Association of CD4+ Radiation-Induced Lymphocyte Apoptosis with Fibrosis and Telangiectasia after Radiotherapy in 272 Breast Cancer Patients with >10-Year Follow-up.Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 15;25(2):562-572. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-0777. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30327309
-
Concurrent or sequential letrozole with adjuvant breast radiotherapy: final results of the CO-HO-RT phase II randomized trial.Ann Oncol. 2016 Mar;27(3):474-80. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv602. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Ann Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26681684 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
RILA blood biomarker as a predictor of radiation-induced sarcoma in a matched cohort study.EBioMedicine. 2019 Mar;41:420-426. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.02.031. Epub 2019 Mar 1. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 30827931 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Radiation-Induced Lymphocyte Apoptosis as a Predictor of Late Toxicity After Breast Radiotherapy.J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2019 Jun;50(2):337-344. doi: 10.1016/j.jmir.2019.02.004. Epub 2019 Apr 15. J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2019. PMID: 31176443
-
[Evidence-based radiotherapy in the treatment of operable breast cancer: results in the 1990-ies].Orv Hetil. 2000 Jul 9;141(28):1551-5. Orv Hetil. 2000. PMID: 10957865 Review. Hungarian.
Cited by
-
Improving Patients' Life Quality after Radiotherapy Treatment by Predicting Late Toxicities.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 22;14(9):2097. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092097. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiodermatitis and Fibrosis in the Context of Breast Radiation Therapy: A Critical Review.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 25;13(23):5928. doi: 10.3390/cancers13235928. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34885037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards Personalized Radiotherapy in Pelvic Cancer: Patient-Related Risk Factors for Late Radiation Toxicity.Curr Oncol. 2025 Jan 17;32(1):47. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32010047. Curr Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39851963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developing Predictive or Prognostic Biomarkers for Charged Particle Radiotherapy.Int J Part Ther. 2018 Summer;5(1):94-102. doi: 10.14338/IJPT-18-00027.1. Int J Part Ther. 2018. PMID: 30393751 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Individual Radiosensitivity in Breast Cancer Patients Using a Combination of Biomolecular Markers.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 7;11(4):1122. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041122. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189740 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Ghazal S.K., Fallowfield L., Blamey R.W. Does cosmetic outcome from treatment of primary breast cancer influence psychosocial morbidity? Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 1999;25(6):571–573. (Epub 1999/11/11) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

