Hepatitis E Virus Superinfection and Clinical Progression in Hepatitis B Patients
- PMID: 26844288
- PMCID: PMC4703726
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.11.020
Hepatitis E Virus Superinfection and Clinical Progression in Hepatitis B Patients
Abstract
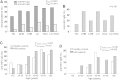
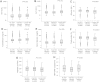
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) infection may cause acute hepatitis and lead to hepatic failure in developing and developed countries. We studied HEV seroprevalences in patients with hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection to understand the consequences of HEV superinfection in a Vietnamese population. This cross-sectional study was conducted from 2012 to 2013 and included 1318 Vietnamese patients with HBV-related liver diseases and 340 healthy controls. The case group included patients with acute (n = 26) and chronic hepatitis B (n = 744), liver cirrhosis (n = 160), hepatocellular carcinoma (n = 166) and patients with both liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (n = 222). Anti-HEV IgG and IgM antibodies were assessed in patients and controls by ELISA. HEV-RNA was identified by PCR assays and sequencing. Seroprevalences of anti-HEV IgG among hepatitis B patients and controls were 45% and 31%, respectively (adjusted P = 0.034). Anti-HEV IgM seroprevalences were 11.6% and 4.7% in patients and controls, respectively (adjusted P = 0.005). Seroprevalences were higher among the elder individuals. When stratifying for patient groups, those with liver cirrhosis had the highest anti-HEV IgG (52%) and anti-HEV IgM (19%) seroprevalences. Hepatitis B patients with current HEV infection had abnormal liver function tests compared to patients with past or without HEV infection. One HEV isolate was retrieved from a patient with both liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma and identified as HEV genotype 3. This study indicates high prevalences of HEV infection in Vietnamese HBV patients and among healthy individuals and shows that HEV superinfection may influence the outcome and progression of HBV-related liver disease.
Keywords: AFP, alpha-feto protein; AHB, acute hepatitis B; ALT, alanine amino transferase; AST, aspartate amino transferase; CHB, chronic hepatitis B; HBV infection; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HBV-related liver diseases; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HEV seroprevalence; HEV superinfection; HEV, hepatitis E virus; Hepatitis E virus; IgG, immunoglobulin G; IgM, immunoglobulin M; LC, liver cirrhosis; ORF, open reading frame; PLT, platelets; RBC, red blood cells; WBC, white blood cells.
Figures

References
-
- Abravanel F., Lhomme S., Chapuy-Regaud S., Mansuy J.M., Muscari F., Sallusto F., Rostaing L., Kamar N., Izopet J. Hepatitis E virus reinfections in solid-organ-transplant recipients can evolve into chronic infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2014;209:1900–1906. - PubMed
-
- Avellon A., Morago L., Garcia-Galera Del C.M., Munoz M., Echevarria J.M. Comparative sensitivity of commercial tests for hepatitis E genotype 3 virus antibody detection. J. Med. Virol. 2015;87:1934–1939. - PubMed
-
- Bayram A., Eksi F., Mehli M., Sozen E. Prevalence of hepatitis E virus antibodies in patients with chronic hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis C. Intervirology. 2007;50:281–286. - PubMed
-
- Beale M.A., Tettmar K., Szypulska R., Tedder R.S., Ijaz S. Is there evidence of recent hepatitis E virus infection in English and North Welsh blood donors? Vox Sang. 2011;100:340–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

