Pancreatic polypeptide and its central Y4 receptors are essential for cued fear extinction and permanent suppression of fear
- PMID: 26844810
- PMCID: PMC4882497
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13456
Pancreatic polypeptide and its central Y4 receptors are essential for cued fear extinction and permanent suppression of fear
Abstract
Background and purpose: Avoiding danger and finding food are closely related behaviours that are essential for surviving in a natural environment. Growing evidence supports an important role of gut-brain peptides in modulating energy homeostasis and emotional-affective behaviour. For instance, postprandial release of pancreatic polypeptide (PP) reduced food intake and altered stress-induced motor activity and anxiety by activating central Y4 receptors.
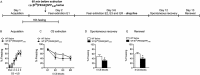
Experimental approach: We characterized [K(30) (PEG2)]hPP2-36 as long-acting Y4 receptor agonist and injected it peripherally into wildtype and Y4 receptor knockout (Y4KO) C57Bl/6NCrl mice to investigate the role of Y4 receptors in fear conditioning. Extinction and relapse after extinction was measured by spontaneous recovery and renewal.
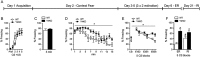
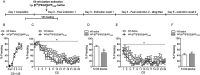
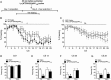
Key results: The Y4KO mice showed impaired cued and context fear extinction without affecting acquisition, consolidation or recall of fear. Correspondingly, peripheral injection of [K(30) (PEG2)]hPP2-36 facilitated extinction learning upon fasting, an effect that was long-lasting and generalized. Furthermore, peripherally applied [K(30) (PEG2)]hPP2-36 before extinction inhibited the activation of orexin-expressing neurons in the lateral hypothalamus in WT, but not in Y4KO mice.
Conclusions and implications: Our findings suggests suppression of excessive arousal as a possible mechanism for the extinction-promoting effect of central Y4 receptors and provide strong evidence that fear extinction requires integration of vegetative stimuli with cortical and subcortical information, a process crucially depending on Y4 receptors. Importantly, in the lateral hypothalamus two peptide systems, PP and orexin, interact to generate an emotional response adapted to the current homeostatic state. Detailed investigations of feeding-relevant genes may thus deliver multiple intervention points for treating anxiety-related disorders.
© 2016 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NPY Y2 receptors in the central amygdala reduce cued but not contextual fear.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Dec;99:665-74. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.08.038. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 26314208
-
Hunger Promotes Fear Extinction by Activation of an Amygdala Microcircuit.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016 Jan;41(2):431-9. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.163. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016. PMID: 26062787 Free PMC article.
-
Y4 receptors and pancreatic polypeptide regulate food intake via hypothalamic orexin and brain-derived neurotropic factor dependent pathways.Neuropeptides. 2010 Jun;44(3):261-8. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2010.01.001. Epub 2010 Feb 8. Neuropeptides. 2010. PMID: 20116098
-
The role of Neuropeptide Y in fear conditioning and extinction.Neuropeptides. 2016 Feb;55:111-26. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2015.09.007. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Neuropeptides. 2016. PMID: 26444585 Review.
-
Illuminating the neuropeptide Y4 receptor and its ligand pancreatic polypeptide from a structural, functional, and therapeutic perspective.Neuropeptides. 2024 Jun;105:102416. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2024.102416. Epub 2024 Feb 24. Neuropeptides. 2024. PMID: 38430725 Review.
Cited by
-
Pancreatic Polypeptide but Not Other Members of the Neuropeptide Y Family Shows a Moderate Association With Perceived Anxiety in Obese Men.Front Hum Neurosci. 2020 Oct 19;14:578578. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2020.578578. eCollection 2020. Front Hum Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33192409 Free PMC article.
-
Illuminating Neuropeptide Y Y4 Receptor Binding: Fluorescent Cyclic Peptides with Subnanomolar Binding Affinity as Novel Molecular Tools.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Mar 20;7(4):1142-1168. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00013. eCollection 2024 Apr 12. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 38633582 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptide Y reduces expression of social fear via simultaneous activation of Y1 and Y2 receptors.J Psychopharmacol. 2019 Dec;33(12):1533-1539. doi: 10.1177/0269881119862529. Epub 2019 Jul 22. J Psychopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31328614 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptide Y Reduces Social Fear in Male Mice: Involvement of Y1 and Y2 Receptors in the Dorsolateral Septum and Central Amygdala.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 20;22(18):10142. doi: 10.3390/ijms221810142. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34576305 Free PMC article.
-
Placental Neuropeptide Y ( NPY) and NPY receptors expressions and serum NPY levels in preeclampsia.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2019 Apr;244(5):380-388. doi: 10.1177/1535370219831437. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2019. PMID: 30760028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acuna‐Goycolea C, Tamamaki N, Yanagawa Y, Obata K, van den Pol AN (2005). Mechanisms of neuropeptide Y, peptide YY, and pancreatic polypeptide inhibition of identified green fluorescent protein‐expressing GABA neurons in the hypothalamic neuroendocrine arcuate nucleus. J Neurosci 25: 7406–7419. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Asakawa A, Inui A, Ueno N, Fujimiya M, Fujino MA, Kasuga M (1999). Mouse pancreatic polypeptide modulates food intake, while not influencing anxiety in mice. Peptides 20: 1445–1448. - PubMed
-
- Asakawa A, Inui A, Yuzuriha H, Ueno N, Katsuura G, Fujimiya M et al. (2003). Characterization of the effects of pancreatic polypeptide in the regulation of energy balance. Gastroenterology 124: 1325–1336. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

