The putative role of Rhipicephalus microplus salivary serpins in the tick-host relationship
- PMID: 26844868
- PMCID: PMC4808628
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2016.01.004
The putative role of Rhipicephalus microplus salivary serpins in the tick-host relationship
Abstract
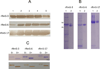
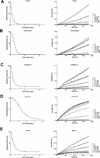
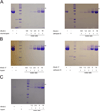
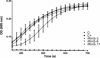
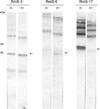
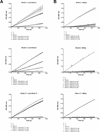
Inflammation and hemostasis are part of the host's first line of defense to tick feeding. These systems are in part serine protease mediated and are tightly controlled by their endogenous inhibitors, in the serpin superfamily (serine protease inhibitors). From this perspective ticks are thought to use serpins to evade host defenses during feeding. The cattle tick Rhipicephalus microplus encodes at least 24 serpins, of which RmS-3, RmS-6, and RmS-17 were previously identified in saliva of this tick. In this study, we screened inhibitor functions of these three saliva serpins against a panel of 16 proteases across the mammalian defense pathway. Our data confirm that Pichia pastoris-expressed rRmS-3, rRmS-6, and rRmS-17 are likely inhibitors of pro-inflammatory and pro-coagulant proteases. We show that rRmS-3 inhibited chymotrypsin and cathepsin G with stoichiometry of inhibition (SI) indices of 1.8 and 2.0, and pancreatic elastase with SI higher than 10. Likewise, rRmS-6 inhibited trypsin with SI of 2.6, chymotrypsin, factor Xa, factor XIa, and plasmin with SI higher than 10, while rRmS-17 inhibited trypsin, cathepsin G, chymotrypsin, plasmin, and factor XIa with SI of 1.6, 2.6, 2.7, 3.4, and 9.0, respectively. Additionally, we observed the formation of irreversible complexes between rRmS-3 and chymotrypsin, rRmS-6/rRmS-17 and trypsin, and rRmS-3/rRmS-17 and cathepsin G, which is consistent with typical mechanism of inhibitory serpins. In blood clotting assays, rRmS-17 delayed plasma clotting by 60 s in recalcification time assay, while rRmS-3 and rRmS-6 did not have any effect. Consistent with inhibitor function profiling data, 2.0 μM rRmS-3 and rRmS-17 inhibited cathepsin G-activated platelet aggregation in a dose-responsive manner by up to 96% and 95% respectively. Of significant interest, polyclonal antibodies blocked inhibitory functions of the three serpins. Also notable, antibodies to Amblyomma americanum, Ixodes scapularis, and Rhipicephalus sanguineus tick saliva proteins cross-reacted with the three R. microplus saliva serpins, suggesting the potential of these proteins as candidates for universal anti-tick vaccines.
Keywords: Cathepsin G; Immune response; Platelet aggregation inhibitor; Tick saliva.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Conserved Amblyomma americanum tick Serpin19, an inhibitor of blood clotting factors Xa and XIa, trypsin and plasmin, has anti-haemostatic functions.Int J Parasitol. 2015 Aug;45(9-10):613-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2015.03.009. Epub 2015 May 5. Int J Parasitol. 2015. PMID: 25957161 Free PMC article.
-
Differential recognition by tick-resistant cattle of the recombinantly expressed Rhipicephalus microplus serine protease inhibitor-3 (RMS-3).Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2012 Jun;3(3):159-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2012.03.002. Epub 2012 May 17. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2012. PMID: 22608113
-
A blood meal-induced Ixodes scapularis tick saliva serpin inhibits trypsin and thrombin, and interferes with platelet aggregation and blood clotting.Int J Parasitol. 2014 May;44(6):369-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2014.01.010. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Int J Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 24583183 Free PMC article.
-
Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus embryo proteins as target for tick vaccine.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2012 Jul 15;148(1-2):149-56. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2011.05.011. Epub 2011 May 7. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2012. PMID: 21620488 Review.
-
Host resistance in cattle to infestation with the cattle tick Rhipicephalus microplus.Parasite Immunol. 2014 Nov;36(11):553-9. doi: 10.1111/pim.12140. Parasite Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25313455 Review.
Cited by
-
Serpin functions in host-pathogen interactions.PeerJ. 2018 Apr 5;6:e4557. doi: 10.7717/peerj.4557. eCollection 2018. PeerJ. 2018. PMID: 29632742 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Omics Technologies Applied to Improve Tick Research.Microorganisms. 2025 Mar 31;13(4):795. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13040795. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40284631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulatory effects of Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides serpin RHS2 on host immune responses.Parasit Vectors. 2019 Jul 11;12(1):341. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3607-4. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 31296257 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of blood meal-responsive serpins prevents Ixodes scapularis from feeding to repletion.Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018 Mar;9(3):506-518. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2018.01.001. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018. PMID: 29396196 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of proteins from the secretory/excretory products (SEPs) of the branchiuran ectoparasite Argulus foliaceus (Linnaeus, 1758) reveals unique secreted proteins amongst haematophagous ecdysozoa.Parasit Vectors. 2020 Feb 18;13(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-3964-z. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 32070416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berger M, Reck J, Jr, Terra RM, Pinto AF, Termignoni C, Guimaraes JA. Lonomia obliqua caterpillar envenomation causes platelet hypoaggregation and blood incoagulability in rats. Toxicon. 2010;55:33–44. - PubMed
-
- Bode W, Meyer E, Jr, Powers JC. Human leukocyte and porcine pancreatic elastase: X-ray crystal structures, mechanism, substrate specificity, and mechanism-based inhibitors. Biochemistry. 1989;28:1951–1963. - PubMed
-
- Brown RE, Jarvis KL, Hyland KJ. Protein measurement using bicinchoninic acid: elimination of interfering substances. Anal. Biochem. 1989;180:136–139. - PubMed
-
- Brown SJ, Galli SJ, Gleich GJ, Askenase PW. Ablation of immunity to Amblyomma americanum by anti-basophil serum: cooperation between basophils and eosinophils in expression of immunity to ectoparasites (ticks) in guinea pigs. J. Immunol. 1982;129:790–796. - PubMed
-
- Burysek L, Syrovets T, Simmet T. The serine protease plasmin triggers expression of MCP-1 and CD40 in human primary monocytes via activation of p38 MAPK and janus kinase (JAK)/STAT signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:33509–33517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

