Influence of Climate Extremes and Land Use on Fecal Contamination of Shallow Tubewells in Bangladesh
- PMID: 26844955
- PMCID: PMC4775353
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.5b05193
Influence of Climate Extremes and Land Use on Fecal Contamination of Shallow Tubewells in Bangladesh
Abstract
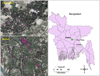
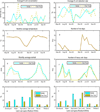
Climate extremes in conjunction with some land use practices are expected to have large impacts on water quality. However, the impacts of land use and climate change on fecal contamination of groundwater has not been well characterized. This work quantifies the influences of extreme weather events and land use practices on Escherichia coli presence and concentration in groundwater from 125 shallow wells, a dominant drinking water resource in rural Bangladesh, monitored over a 17 month period. The results showed that E. coli presence was significantly associated with the number of heavy rain days, developed land and areas with more surface water. These variables also had significant impacts on E. coli concentration, with risk ratios of 1.38 (95% CI = 1.16, 1.65), 1.07 (95% CI: 1.05, 1.09), and 1.02 (95% CI = 1.01, 1.03), respectively. Significant synergistic effects on E. coli presence and concentration were observed when land use and weather variables were combined. The findings suggest that climate extremes and land use practices, particularly urbanization, might promote fecal contamination of shallow well water, thus increasing the risk of diarrheal diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Bates B, Kundzewicz ZW, Wu S, Palutikof J. climate change and Water: technical Paper vi. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC); 2008.
-
- Foley JA, DeFries R, Asner GP, Barford C, Bonan G, Carpenter SR, Chapin FS, Coe MT, Daily GC, Gibbs HK. Global consequences of land use. Science. 2005;309(5734):570–574. - PubMed
-
- Paule MCA, Ventura J-RS, Memon S, Lee B-Y, Jahng D, Kang M-J, Lee C-H. Fecal contamination in Yongin watershed: association to land use and land cover and stormwater quality. Desalination Water Treat. 2015;53(11):3026–3038.
-
- Vernberg W, Scott G, Strozier S, Bemiss J, Daugomah J. The effects of urbanization on human and ecosystem health. In: Vernberg F, Vernberg W, Siewicki T, editors. Sustainable Development in the Southeastern Coastal Zone. Columbia, SC: The University of South Carolina Press; 1996. 1996. pp. 221–239.
-
- Foster SS. Impacts of urbanization on groundwater, Hydrological processes and water management in urban areas. Wallingford, UK: International Association of Hydrological Sciences–Association Internationale des Sciences Hydrologiques; 1990. (IAHS–AISH Pub. No. 198)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

