Discovery of Novel Hepatitis C Virus NS5B Polymerase Inhibitors by Combining Random Forest, Multiple e-Pharmacophore Modeling and Docking
- PMID: 26845440
- PMCID: PMC4742222
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148181
Discovery of Novel Hepatitis C Virus NS5B Polymerase Inhibitors by Combining Random Forest, Multiple e-Pharmacophore Modeling and Docking
Abstract
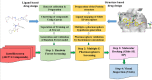
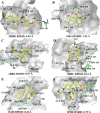
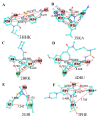
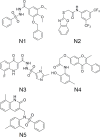
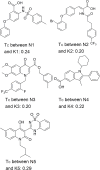
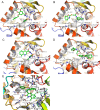
The NS5B polymerase is one of the most attractive targets for developing new drugs to block Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. We describe the discovery of novel potent HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitors by employing a virtual screening (VS) approach, which is based on random forest (RB-VS), e-pharmacophore (PB-VS), and docking (DB-VS) methods. In the RB-VS stage, after feature selection, a model with 16 descriptors was used. In the PB-VS stage, six energy-based pharmacophore (e-pharmacophore) models from different crystal structures of the NS5B polymerase with ligands binding at the palm I, thumb I and thumb II regions were used. In the DB-VS stage, the Glide SP and XP docking protocols with default parameters were employed. In the virtual screening approach, the RB-VS, PB-VS and DB-VS methods were applied in increasing order of complexity to screen the InterBioScreen database. From the final hits, we selected 5 compounds for further anti-HCV activity and cellular cytotoxicity assay. All 5 compounds were found to inhibit NS5B polymerase with IC50 values of 2.01-23.84 μM and displayed anti-HCV activities with EC50 values ranging from 1.61 to 21.88 μM, and all compounds displayed no cellular cytotoxicity (CC50 > 100 μM) except compound N2, which displayed weak cytotoxicity with a CC50 value of 51.3 μM. The hit compound N2 had the best antiviral activity against HCV, with a selective index of 32.1. The 5 hit compounds with new scaffolds could potentially serve as NS5B polymerase inhibitors through further optimization and development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multiple e-pharmacophore modeling, 3D-QSAR, and high-throughput virtual screening of hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase inhibitors.J Chem Inf Model. 2014 Feb 24;54(2):539-52. doi: 10.1021/ci400644r. Epub 2014 Feb 5. J Chem Inf Model. 2014. PMID: 24460140
-
Multiple virtual screening approaches for finding new hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors: structure-based screens and molecular dynamics for the pursue of new poly pharmacological inhibitors.BMC Bioinformatics. 2012;13 Suppl 17(Suppl 17):S5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-S17-S5. Epub 2012 Dec 13. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 23282180 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel inhibitors of HCV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase by pharmacophore-based virtual screening and in vitro evaluation.Bioorg Med Chem. 2009 Apr 15;17(8):2975-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2009.03.024. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19332375
-
Current perspective of HCV NS5B inhibitors: a review.Curr Med Chem. 2011;18(36):5564-97. doi: 10.2174/092986711798347234. Curr Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 22172066 Review.
-
New NS5B polymerase inhibitors for hepatitis C.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010 Aug;19(8):963-75. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2010.500285. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20629614 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of NS2B-NS3 Protease Inhibitors for Therapeutic Application in ZIKV Infection: A Pharmacophore-Based High-Throughput Virtual Screening and MD Simulations Approaches.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jan 5;11(1):131. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11010131. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679976 Free PMC article.
-
Immuno-Informatics Analysis of Pakistan-Based HCV Subtype-3a for Chimeric Polypeptide Vaccine Design.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Mar 21;9(3):293. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9030293. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33801143 Free PMC article.
-
A Random Forest Model for Peptide Classification Based on Virtual Docking Data.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 13;24(14):11409. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411409. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511165 Free PMC article.
-
In silico identification of novel SARS-COV-2 2'-O-methyltransferase (nsp16) inhibitors: structure-based virtual screening, molecular dynamics simulation and MM-PBSA approaches.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021 Dec;36(1):727-736. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2021.1885396. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33685335 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Model for HCVNS5B inhibitors based on an Antlion Optimizer-Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 24;8(1):1506. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-19122-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29367667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Hepatitis C. Fact sheet no.164, 2014. Available: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs164/en/. Accessed 10 September 2014.
-
- HEP: Available: http://www.hepmag.com/drug_list_hepatitisc.shtml. Accessed 17 September 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

