Recombinational branch migration by the RadA/Sms paralog of RecA in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 26845522
- PMCID: PMC4786428
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.10807
Recombinational branch migration by the RadA/Sms paralog of RecA in Escherichia coli
Abstract
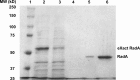
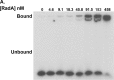
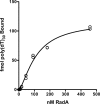
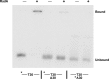
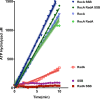
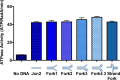
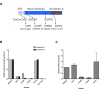
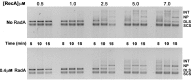
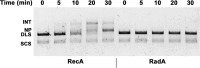
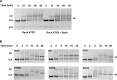
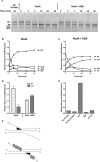
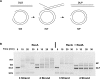
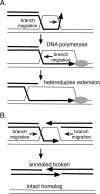
RadA (also known as 'Sms') is a highly conserved protein, found in almost all eubacteria and plants, with sequence similarity to the RecA strand exchange protein and a role in homologous recombination. We investigate here the biochemical properties of the E. coli RadA protein and several mutant forms. RadA is a DNA-dependent ATPase, a DNA-binding protein and can stimulate the branch migration phase of RecA-mediated strand transfer reactions. RadA cannot mediate synaptic pairing between homologous DNA molecules but can drive branch migration to extend the region of heteroduplex DNA, even without RecA. Unlike other branch migration factors RecG and RuvAB, RadA stimulates branch migration within the context of the RecA filament, in the direction of RecA-mediated strand exchange. We propose that RadA-mediated branch migration aids recombination by allowing the 3' invading strand to be incorporated into heteroduplex DNA and to be extended by DNA polymerases.
Keywords: e. coli; DNA damage response; DNA mutagenesis; DNA repair; chromosomes; double-strand break repair; genes; homologous recombination; infectious disease; microbiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures


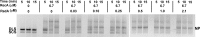
Similar articles
-
Genetic analysis of Escherichia coli RadA: functional motifs and genetic interactions.Mol Microbiol. 2015 Mar;95(5):769-79. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12899. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Mol Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25484163 Free PMC article.
-
Role for radA/sms in recombination intermediate processing in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2002 Dec;184(24):6836-44. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.24.6836-6844.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12446634 Free PMC article.
-
Replication arrest-stimulated recombination: Dependence on the RecA paralog, RadA/Sms and translesion polymerase, DinB.DNA Repair (Amst). 2006 Dec 9;5(12):1421-7. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.06.008. Epub 2006 Aug 9. DNA Repair (Amst). 2006. PMID: 16904387
-
Unraveling the late stages of recombinational repair: metabolism of DNA junctions in Escherichia coli.Bioessays. 1996 Sep;18(9):757-65. doi: 10.1002/bies.950180911. Bioessays. 1996. PMID: 8831292 Review.
-
Relating biochemistry to biology: how the recombinational repair function of RecA protein is manifested in its molecular properties.Bioessays. 1993 Sep;15(9):617-23. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150908. Bioessays. 1993. PMID: 8240315 Review.
Cited by
-
Life, the genome and everything.J Bacteriol. 2023 Dec 19;205(12):e0027223. doi: 10.1128/jb.00272-23. Epub 2023 Nov 29. J Bacteriol. 2023. PMID: 38018999 Free PMC article.
-
Escherichia coli RadD Protein Functionally Interacts with the Single-stranded DNA-binding Protein.J Biol Chem. 2016 Sep 23;291(39):20779-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.736223. Epub 2016 Aug 12. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27519413 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Function Analysis Reveals the Singularity of Plant Mitochondrial DNA Replication Components: A Mosaic and Redundant System.Plants (Basel). 2019 Nov 21;8(12):533. doi: 10.3390/plants8120533. Plants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31766564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA Repair and the Stability of the Plant Mitochondrial Genome.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 3;21(1):328. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010328. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31947741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RadB acts in homologous recombination in the archaeon Haloferax volcanii, consistent with a role as recombination mediator.DNA Repair (Amst). 2017 Jul;55:7-16. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2017.04.005. Epub 2017 Apr 26. DNA Repair (Amst). 2017. PMID: 28501701 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

