Developmental expression of Kv1 voltage-gated potassium channels in the avian hypothalamus
- PMID: 26845562
- PMCID: PMC6262825
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.01.068
Developmental expression of Kv1 voltage-gated potassium channels in the avian hypothalamus
Abstract
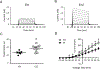
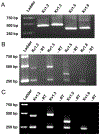
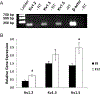
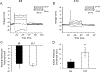
Specialized hypothalamic neurons integrate the homeostatic balance between food intake and energy expenditure, processes that may become dysregulated during the development of diabetes, obesity, and other metabolic disorders. Shaker family voltage-gated potassium channels (Kv1) contribute to the maintenance of resting membrane potential, action potential characteristics, and neurotransmitter release in many populations of neurons, although hypothalamic Kv1 channel expression has been largely unexplored. Whole-cell patch clamp recordings from avian hypothalamic brain slices demonstrate a developmental shift in the electrophysiological properties of avian arcuate nucleus neurons, identifying an increase in outward ionic current that corresponds with action potential maturation. Additionally, RT-PCR experiments identified the early expression of Kv1.2, Kv1.3, and Kv1.5 mRNA in the embryonic avian hypothalamus, suggesting that these channels may underlie the electrophysiological changes observed in these neurons. Real-time quantitative PCR analysis on intact microdissections of embryonic hypothalamic tissue revealed a concomitant increase in Kv1.2 and Kv1.5 gene expression at key electrophysiological time points during development. This study is the first to demonstrate hypothalamic mRNA expression of Kv1 channels in developing avian embryos and may suggest a role for voltage-gated ion channel regulation in the physiological patterning of embryonic hypothalamic circuits governing energy homeostasis.
Keywords: Development; Embryonic chicken; Energy homeostasis; Hypothalamus; Kv1; Potassium channel.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
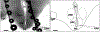
Similar articles
-
Studies of Conorfamide-Sr3 on Human Voltage-Gated Kv1 Potassium Channel Subtypes.Mar Drugs. 2020 Aug 13;18(8):425. doi: 10.3390/md18080425. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32823677 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental change in expression and subcellular localization of two shaker-related potassium channel proteins (Kv1.1 and Kv1.2) in the chick tangential vestibular nucleus.J Comp Neurol. 2003 Jul 7;461(4):466-82. doi: 10.1002/cne.10702. J Comp Neurol. 2003. PMID: 12746863
-
Kv1 channels regulate variations in spike patterning and temporal reliability in the avian cochlear nucleus angularis.J Neurophysiol. 2022 Jan 1;127(1):116-129. doi: 10.1152/jn.00460.2021. Epub 2021 Nov 24. J Neurophysiol. 2022. PMID: 34817286 Free PMC article.
-
The Olfactory Bulb: A Metabolic Sensor of Brain Insulin and Glucose Concentrations via a Voltage-Gated Potassium Channel.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2010;52:147-57. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-14426-4_12. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2010. PMID: 20865378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marine Toxins Targeting Kv1 Channels: Pharmacological Tools and Therapeutic Scaffolds.Mar Drugs. 2020 Mar 20;18(3):173. doi: 10.3390/md18030173. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32245015 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin receptor localization in the embryonic avian hypothalamus.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Apr 17;698:126-132. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.01.009. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 30615976 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gutman GA, Chandy KG, Grissmer S, Lazdunski M, Mckinnon D, Pardo LA, et al., International Union of Pharmacology. LIII. Nomenclature and molecular relationships of voltage-gated potassium channels. Pharmacological Reviews 57 (2005) 473–508. - PubMed
-
- Hille B, Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes, first ed., Sunderland, Massachusettes, 1984.
-
- Sutachan JJ, Watanabe I, Zhu J, Gottschalk A, Recio-Pinto E, Thornhill WB, Effects of Kv1.1 channel glycosylation on C-type inactivation and simulated action potentials. Brain Res 1058 (2005) 30–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

