Telmisartan in the diabetic murine model of acute myocardial infarction: dual contrast manganese-enhanced and delayed enhancement MRI evaluation of the peri-infarct region
- PMID: 26846539
- PMCID: PMC4743104
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-016-0348-y
Telmisartan in the diabetic murine model of acute myocardial infarction: dual contrast manganese-enhanced and delayed enhancement MRI evaluation of the peri-infarct region
Abstract
Background: A novel MRI technique, employing dual contrast manganese-enhanced MRI (MEMRI) and delayed enhancement MRI (DEMRI), can evaluate the physiologically unstable peri-infarct region. Dual contrast MEMRI-DEMRI enables comprehensive evaluation of telmisartan to salvage the peri-infarct injury to elucidate the underlying mechanism of restoring the ischemic cardiomyopathy in the diabetic mouse model.
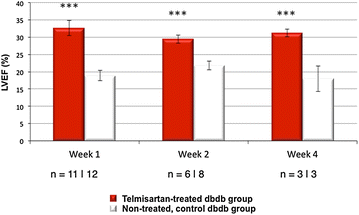
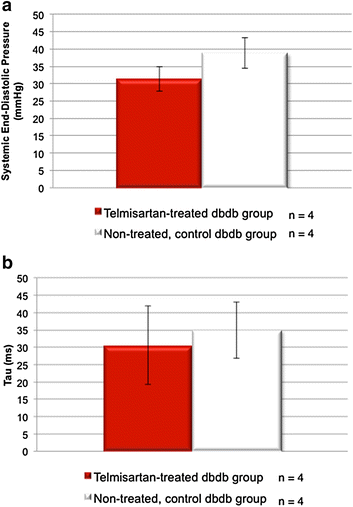
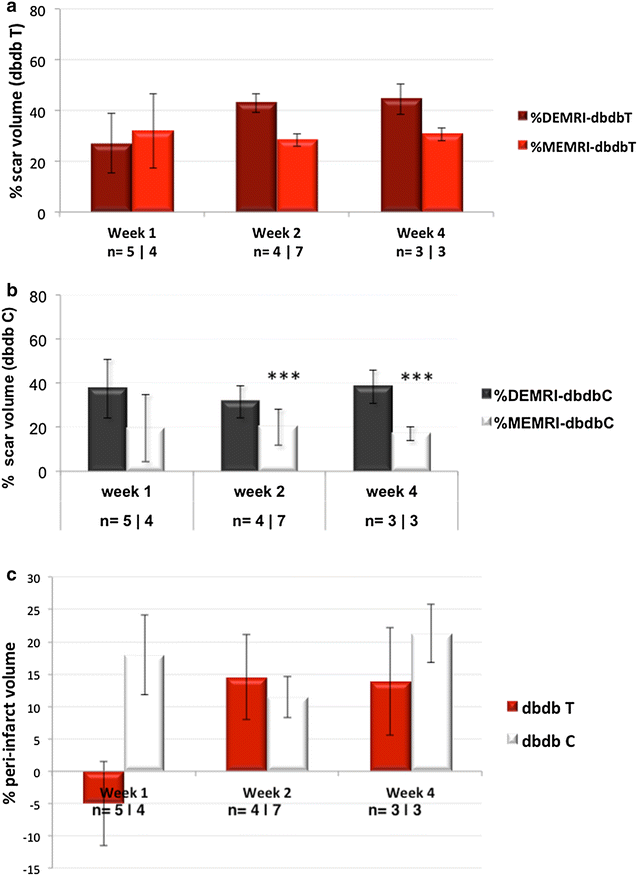
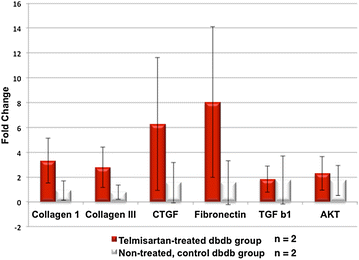
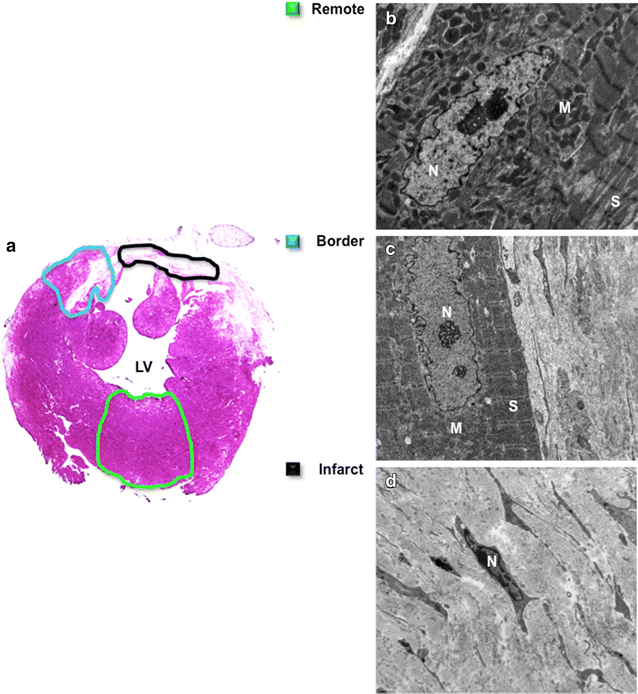
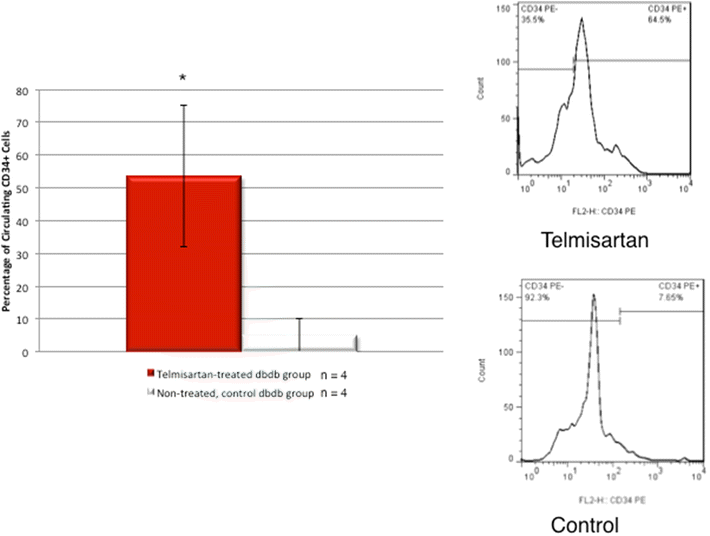
Methods and results: Dual contrast MEMRI-DEMRI was performed on weeks 1, 2, and 4 following initiation of telmisartan treatment in 24 left anterior descendent artery ligated diabetic mice. The MRI images were analyzed for core infarct, peri-infarct, left ventricular end-diastolic, end-systolic volumes, and the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and real-time PCR were used for ex vivo analysis of the myocardium. Telmisartan vs. control groups demonstrated significantly improved LVEF at weeks 1, 2, and 4, respectively (33 ± 7 %*** vs. 19 ± 5 %, 29 ± 3 %*** vs. 22 ± 4 %, and 31 ± 2 %*** vs 18 ± 6 %, ***p < 0.001). The control group demonstrated significant differences in the scar volume measured by MEMRI and DEMRI, demonstrating peri-infarct injury. Telmisartan group significantly salvaged the peri-infarct injury. The myocardial effects were validated by TEM, which confirmed the presence of the injured but viable cardiomyocyte morphology in the peri-infarct region and by flow cytometry of venous blood, which demonstrated significantly increased circulating endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs).
Conclusion: The improved cardiac function in ischemic cardiomyopathy of diabetic mice by telmisartan is attributed to the attenuation of the peri-infarct injury by the angiogenic effects of EPCs to salvage the injured cardiomyocytes. Dual-contrast MEMRI-DEMRI technique tracked the therapeutic effects of telmisartan on the injured myocardium longitudinally.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dual manganese-enhanced and delayed gadolinium-enhanced MRI detects myocardial border zone injury in a pig ischemia-reperfusion model.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011 Sep;4(5):574-82. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.110.960591. Epub 2011 Jun 30. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011. PMID: 21719779 Free PMC article.
-
Manganese-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Enables In Vivo Confirmation of Peri-Infarct Restoration Following Stem Cell Therapy in a Porcine Ischemia-Reperfusion Model.J Am Heart Assoc. 2015 Jul 27;4(7):e002044. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002044. J Am Heart Assoc. 2015. PMID: 26215972 Free PMC article.
-
Different roles of PPAR-γ activity on physiological and pathological alteration after myocardial ischemia.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2012 Aug;60(2):158-64. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3182592d7b. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22561360
-
Manganese-enhanced MRI of the myocardium.Heart. 2019 Nov;105(22):1695-1700. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2019-315227. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Heart. 2019. PMID: 31337670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiogenesis after acute myocardial infarction.Cardiovasc Res. 2021 Apr 23;117(5):1257-1273. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa287. Cardiovasc Res. 2021. PMID: 33063086 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulating mitochondrial dynamics attenuates cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury in prediabetic rats.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022 Jan;43(1):26-38. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00626-3. Epub 2021 Mar 12. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022. PMID: 33712720 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of telmisartan on vascular endothelial function, inflammation and insulin resistance in patients with coronary heart disease and diabetes mellitus.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Jan;15(1):909-913. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5451. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29399098 Free PMC article.
-
MnO nanoparticles with potential application in magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery for myocardial infarction.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Oct 8;13:6177-6188. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S176404. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30323598 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial Viability Imaging using Manganese-Enhanced MRI in the First Hours after Myocardial Infarction.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Jun;8(11):e2003987. doi: 10.1002/advs.202003987. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34105284 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging in experimental models of diabetes.Acta Diabetol. 2022 Feb;59(2):147-161. doi: 10.1007/s00592-021-01826-3. Epub 2021 Nov 15. Acta Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 34779949 Review.
References
-
- Cea Soriano L, Johansson S, Stefansson B, Rodriguez LA. Cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in a cohort of 57,946 patients with type 2 diabetes: associations with renal function and cardiovascular risk factors. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015;14:38. doi: 10.1186/s12933-015-0204-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mercier K, Smith H, Biederman J. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibition: overview of the therapeutic use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, and direct renin inhibitors. Prim Care. 2014;41(4):765–778. doi: 10.1016/j.pop.2014.08.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

